 6 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of biological sciences”
6 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of biological sciences” Removing the ROBO4 gene in mice reduces skin inflammation and hair loss by affecting certain inflammation pathways and gene expression.
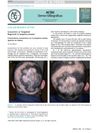 April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that a unique target-like hair regrowth pattern in alopecia areata may be more common than thought and should be properly identified.
 102 citations,
September 1977 in “The Lancet”
102 citations,
September 1977 in “The Lancet” Minoxidil with propranolol and diuretics lowers blood pressure but causes fluid retention and hair growth.
 31 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of endocrinological investigation”
31 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of endocrinological investigation” Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome often causes sexual development issues, hair loss, learning disabilities, deafness, muscle contractions, limb pain, and diabetes.
 64 citations,
June 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
64 citations,
June 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Pregnancy often causes skin changes like darkening, stretch marks, and hair growth, which may improve after childbirth.
 22 citations,
March 1932 in “Journal of the American Medical Association”
22 citations,
March 1932 in “Journal of the American Medical Association” Thallium poisoning from contaminated tortillas caused severe symptoms and was mostly fatal or led to long-term health issues.
 2 citations,
June 2006 in “Experimental dermatology”
2 citations,
June 2006 in “Experimental dermatology” Skin patterns form through molecular signals and genetic factors, affecting healing and dermatology.
 117 citations,
November 2006 in “Experimental Dermatology”
117 citations,
November 2006 in “Experimental Dermatology” The article concludes that the wool follicle is a valuable model for studying tissue interactions and has potential for genetic improvements in wool production.
 79 citations,
September 2009 in “Pediatric dermatology”
79 citations,
September 2009 in “Pediatric dermatology” The 308-nm Excimer laser is effective and safe for treating patchy alopecia areata in children.
 35 citations,
November 1931 in “Journal of Genetics”
35 citations,
November 1931 in “Journal of Genetics” Hairless mice lack fur due to a genetic mutation affecting skin response, not hormone issues.
 24 citations,
November 2016 in “Cell death and disease”
24 citations,
November 2016 in “Cell death and disease” Skin-derived stem cells can become various cell types, including germ cell-like and oocyte-like cells.
 24 citations,
September 2008 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
24 citations,
September 2008 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Repigmentation in vitiligo may come from melanocyte stem cells in the skin.
22 citations,
January 2009 in “Advances in experimental medicine and biology” FOXN1 mutations cause severe immunodeficiency, hair loss, nail issues, and thymus defects.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Bone”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Bone” Removing a methyl group from the ITGAV gene speeds up bone formation in a specific type of bone disease model.
6 citations,
October 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair splitting and nail detachment are linked conditions.
 5 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of Clinical Hypertension”
5 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of Clinical Hypertension” Men with severe early-onset baldness may have worse heart artery function and stiffer arteries if they have high blood pressure.
 2 citations,
February 2024 in “Nature cell biology”
2 citations,
February 2024 in “Nature cell biology” Mechanical forces are crucial for shaping cells and forming tissues during development.
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Treatment with methotrexate and prednisolone led to complete hair regrowth and no relapse for 2 years.
 April 2023 in “Advanced functional materials”
April 2023 in “Advanced functional materials” The study created a tool that mimics natural cell signals, which increased cell growth and could help with hair regeneration research.
 January 2023 in “Clinical dermatology review”
January 2023 in “Clinical dermatology review” COVID-19 infection may cause hair loss.

Low-level laser therapy may help stem cells grow and function better, aiding in healing and tissue repair.
 299 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation”
299 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” Different types of fibroblasts play various roles in diseases and healing, and more research on them could improve treatments.
 277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The skin's layers protect, sense, and regulate the body's internal balance, but can be prone to cancer.
 208 citations,
July 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
208 citations,
July 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause various skin changes and diseases, with PUPPP being the most common skin condition specific to pregnancy.
 188 citations,
March 2018 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
188 citations,
March 2018 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Regulatory T-cells are important for healing and regenerating tissues in various organs by controlling immune responses and aiding stem cells.
 187 citations,
December 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
187 citations,
December 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” Estrogens can improve skin aging but carry risks; more research is needed on safer treatments.
 182 citations,
August 2016 in “Development”
182 citations,
August 2016 in “Development” ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes are crucial for gene regulation, cell differentiation, and organ development in mammals.
 178 citations,
August 2016 in “Advances in wound care”
178 citations,
August 2016 in “Advances in wound care” New effective scar treatments are urgently needed due to the current options' limited success.
 176 citations,
August 1981 in “JAMA”
176 citations,
August 1981 in “JAMA” Toxic Shock Syndrome mainly affects menstruating women, can recur, and is linked to staph bacteria, with rapid treatment being crucial.
 129 citations,
May 2015 in “Cell Stem Cell”
129 citations,
May 2015 in “Cell Stem Cell” Different types of stem cells exist within individual skin layers, and they can adapt to damage, transplantation, or tumor growth. These cells are regulated by their environment and genetic factors. Tumor growth is driven by expanding, genetically altered cells, not long-lived mutant stem cells. There's evidence of cancer stem cells in skin tumors. Other cells, bacteria, and genetic factors help maintain balance and contribute to disease progression. A method for growing mini organs from single cells has been developed.


























