M-CSF-stimulated myeloid cells can turn into skin cells and help heal wounds and regrow hair.
 3 citations,
May 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The book "Dermatology" has useful content but some sections lack detail and accuracy; it's recommended for dermatologists to review before buying.
[object Object]  52 citations,
February 2018 in “Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome”
52 citations,
February 2018 in “Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome” Some skin conditions may indicate metabolic syndrome, which could help with early detection and management of related health issues.
 5 citations,
February 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology”
5 citations,
February 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology” Eating more protein during fast weight loss can prevent hair loss.
 30 citations,
January 2023 in “EFSA journal”
30 citations,
January 2023 in “EFSA journal” Adults should not consume more than 255 micrograms of selenium per day to avoid risk of hair loss and other side effects.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Eating a balanced diet with specific nutrients can help manage menopause symptoms and prevent related health issues.
January 2016 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Hormonal therapy changes skin and hair in transgender patients, who need better researched dermatologic care.
 October 2023 in “Georgetown medical review”
October 2023 in “Georgetown medical review” Finasteride and Dutasteride can improve hair growth in male baldness but may cause temporary sexual dysfunction and possibly affect fertility.
 60 citations,
December 2015 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
60 citations,
December 2015 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Low-level laser therapy is safe and can increase hair growth for male and female pattern hair loss.
 12 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
12 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” COVID-19 patients may experience temporary hair loss, mainly in women, which is likely reversible.
 7 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology”
7 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology” The document concludes that patients with skin of color need specialized dermatological care and education to manage unique skin conditions effectively.
[object Object]  9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications”
9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications” Rare changes in the KRT82 gene are linked to a higher risk of Alopecia Areata.
 397 citations,
February 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
397 citations,
February 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil boosts hair growth by opening potassium channels and increasing cell activity.
 1 citations,
April 2022 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2022 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Classifying curl patterns might help doctors assess and treat hair loss better.
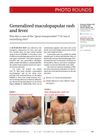 July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice”
July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice” The man was diagnosed with lupus and improved with treatment.
 October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The gene Foxn1 is important for hair growth, and understanding it may lead to new alopecia treatments.

Botox is effective for urinary incontinence, chronic migraines, and male pattern hair loss, and a new test for Botox antibodies is more humane.
 November 2021 in “Dermatology Research and Practice”
November 2021 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” The study aims to understand the skin and hair characteristics of mothers and their babies, and how these may affect newborns' skin health and mothers' postpartum hair loss.
 February 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair loss is a common, often overlooked side effect of hormone treatments for breast and prostate cancer.
 1 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of endocrinology and diabetes”
1 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of endocrinology and diabetes” Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and its causes can lead to effective treatments.
 May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman with Parry-Romberg syndrome developed new curly hair on one side of her scalp, a condition not previously linked to the syndrome.
 November 2024 in “Dermatitis”
November 2024 in “Dermatitis” Men's personal care products often cause allergic skin reactions.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology” Alopecia areata causes unpredictable hair loss and emotional distress, with no cure and limited treatment options.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair loss patterns differ between males and females due to 5 master regulators and JAK-STAT signaling affects hair growth.
 June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Red clover extract-based scalp treatments significantly improved hair volume and reduced hair loss and damage.
 10 citations,
August 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
10 citations,
August 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Decorin helps hair cells grow and move, and keeps hair growth phase going in mice.
 122 citations,
April 2011 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics”
122 citations,
April 2011 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics” Particles around 100 nm can penetrate and stay in hair follicles without passing through healthy skin, making them safe for use in topical products and useful for targeted drug delivery.
 11 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatology and therapy”
11 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatology and therapy” Researchers created a new tool to measure the effects of alopecia areata from the patient's view, focusing on hair loss, daily life, and emotional health.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Zinc deficiency disrupts hair growth and cycle, but zinc supplements can fix this.
9 citations,
October 2015 in “Cutaneous and ocular toxicology” Vemurafenib can cause scalp issues but can be managed without changing the dose.


























