 56 citations,
February 2006 in “American journal of physiology. Cell physiology”
56 citations,
February 2006 in “American journal of physiology. Cell physiology” Steroid sex hormones activate matriptase in prostate cancer cells but not in breast cancer cells.
 34 citations,
March 2003 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
34 citations,
March 2003 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Most dogs with alopecia had higher than normal levels of certain hormones, but hair loss might not always be linked to these hormone changes.
[object Object]  33 citations,
January 2017 in “Conservation physiology”
33 citations,
January 2017 in “Conservation physiology” Measuring reproductive hormones in brown bear hair could help identify their sex and reproductive state, but better collection methods or lab techniques are needed.
 24 citations,
January 1989 in “Archives of biochemistry and biophysics”
24 citations,
January 1989 in “Archives of biochemistry and biophysics” Male rats have androgen receptors in their liver, which are different from proteins that bind estrogen.
 6 citations,
September 2014 in “Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A”
6 citations,
September 2014 in “Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A” New method effectively detects illegal hormones in anti-aging foods.
 1 citations,
October 2023 in “Frontiers in endocrinology”
1 citations,
October 2023 in “Frontiers in endocrinology” Regulating certain sex hormones may help delay facial aging.
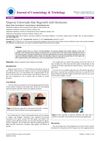 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 May 2024 in “Journal of drug delivery and therapeutics”
May 2024 in “Journal of drug delivery and therapeutics” Women with PCOS have higher oxidative stress and hormone imbalances, suggesting managing oxidative stress could help.
 July 2021 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
July 2021 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Alopecia patients have less GPER-1, which might affect hair loss.
[object Object]  31 citations,
May 2012 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
31 citations,
May 2012 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Menopause affects hair and skin; more research needed for treatment.
Estrogen and its receptors play a key role in hair growth, with differences between males and females.
 9 citations,
August 1952 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
9 citations,
August 1952 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” A 17-year-old female with adrenogenital syndrome produces very high levels of androgens, which prevent complete feminization despite high estrogen doses.
 November 2004 in “Medical Journal of Indonesia”
November 2004 in “Medical Journal of Indonesia” Hormonal imbalances can cause skin and hair problems in women, and treatments that block male hormones can help.
 137 citations,
June 2005 in “Climacteric”
137 citations,
June 2005 in “Climacteric” Estrogen loss during menopause worsens skin health, but hormone replacement therapy may improve it, though more research is needed.
 60 citations,
April 2010 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology”
60 citations,
April 2010 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology” Fadrozole and finasteride change gene expression related to sex hormones and thyroid hormones in frog larvae development.
 47 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders”
47 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders” The skin's ability to produce hormones is linked to various skin conditions, and better understanding this process could lead to new treatments.
 44 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
44 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The effects of estrogen on human hair growth are unclear and need more research.
 41 citations,
November 2003 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
41 citations,
November 2003 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” Male hormones, or androgens, affect women's health in areas like mood and bone density, and hormone replacement therapy using antiandrogenic progestogens can improve mood disorders and alertness in menopausal women.
 30 citations,
March 2001 in “Environmental Health Perspectives”
30 citations,
March 2001 in “Environmental Health Perspectives” Small changes in hormones can significantly impact health, showing the importance of sensitive testing for chemicals that disrupt hormones.
 23 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
23 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” FPHL causes hair loss in women due to genetics and hormones; minoxidil and anti-androgens are treatments, and early intervention is advised.
 23 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation”
23 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation” Sex hormones affect hair and feather growth and may help manage alopecia and hormone-dependent cancers.
 20 citations,
July 2006 in “Veterinary dermatology”
20 citations,
July 2006 in “Veterinary dermatology” Melatonin helped some Pomeranian dogs regrow hair, but it wasn't linked to estrogen receptors.
 10 citations,
April 2018 in “Maturitas”
10 citations,
April 2018 in “Maturitas” Excess male hormones in postmenopausal women can cause health issues and increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes; treatment depends on the cause.
8 citations,
April 2022 in “Trends in cancer” Hormone therapy affects cancer risks in transgender individuals differently than in cisgender people, and more research is needed to understand these risks and improve cancer screening guidelines.
 5 citations,
June 2004 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society”
5 citations,
June 2004 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society” Testosterone therapy can improve sexual satisfaction and mood in surgically menopausal women when used with estrogen, but its long-term safety and effects on naturally menopausal and premenopausal women are unclear.
 3 citations,
July 1990 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
3 citations,
July 1990 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” A man's baldness improved possibly due to a medication that blocks male hormones.
 1 citations,
November 2019 in “Archives of breast cancer”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “Archives of breast cancer” Some hormone treatments might raise breast cancer risk, while others don't seem to.

A mix of Polygonatum sibiricum and Nelumbinis semen may ease menopause symptoms with fewer side effects.
154 citations,
October 1996 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Estrogen affects hair growth and skin cell multiplication.
 150 citations,
April 2013 in “Dermato-endocrinology”
150 citations,
April 2013 in “Dermato-endocrinology” Estrogen therapy can reduce skin aging but has cancer risks.



























