 28 citations,
July 2015 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
28 citations,
July 2015 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” People with Lichen Planus, especially with mucosal involvement, are more likely to have Metabolic Syndrome, which increases their risk for heart disease and diabetes.
 19 citations,
November 2021 in “Lupus Science & Medicine”
19 citations,
November 2021 in “Lupus Science & Medicine” Black patients with discoid lupus erythematosus have more severe skin damage and higher chances of dyspigmentation, scalp, and ear involvement.
15 citations,
February 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” Leptin, a hormone from fat cells, affects immune responses and can influence skin diseases and hair growth.
 11 citations,
September 2022 in “The Journal of Rheumatology”
11 citations,
September 2022 in “The Journal of Rheumatology” Skin problems are common in lupus patients and should be treated early to prevent worsening.
 2 citations,
February 2024 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
February 2024 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The study created a 27-item measure to assess the impact of skin diseases.
 2 citations,
January 2021 in “Scandinavian Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychology”
2 citations,
January 2021 in “Scandinavian Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychology” Kids with skin problems are more likely to have mental health issues.
 July 2024 in “Indonesian Journal of Case Reports”
July 2024 in “Indonesian Journal of Case Reports” Effective treatment improved skin and overall symptoms in a lupus patient.
 October 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
October 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Patients with skin diseases rated psychological effects as most impactful, needing a treatment approach that addresses both mind and body.
 June 2022 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology”
June 2022 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology” The COVID-19 quarantine in Turkey disrupted dermatological care, increased stress-related skin issues, and showed the need for psychological support and teledermatology.
March 2018 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Transplant patients face higher skin cancer risks due to immunosuppressive therapy, requiring careful skin health monitoring.
 June 1930 in “Archives of dermatology”
June 1930 in “Archives of dermatology” Dermatological conditions are complex, and treatments have mixed results.
22 citations,
August 2020 in “Cells” TGM3 is important for skin and hair structure and may help diagnose cancer.
11 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Virology” Older age, pre-existing skin conditions, cirrhosis, and pegylated interferon use increase the risk of skin issues during hepatitis C treatment.
86 citations,
November 2020 in “Annals of Oncology” Early intervention and tailored management can reduce skin side effects from cancer treatments.
 4 citations,
November 2019 in “Biomedical Journal of Scientific and Technical Research”
4 citations,
November 2019 in “Biomedical Journal of Scientific and Technical Research” The document concludes that the acoustic coupler SF-001 is good for skin ultrasound, especially on rough body parts, because it's stable and shows blood vessels well.
 4 citations,
March 2009 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
March 2009 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The conference highlighted new dermatological treatments and emphasized early intervention and addressing conditions lacking evidence-based treatments.
1 citations,
May 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Depression and skin autoimmune diseases are linked, needing combined care for better treatment.
October 2021 in “European journal of cancer” Repeated biopsies are crucial for managing lupus panniculitis when initial treatments fail.
 7 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology”
7 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology” The document concludes that patients with skin of color need specialized dermatological care and education to manage unique skin conditions effectively.
 6 citations,
May 2022 in “Medicina-lithuania”
6 citations,
May 2022 in “Medicina-lithuania” IMA may indicate oxidative stress in skin and hair disorders, but more research is needed.
 July 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Treating skin conditions with both psychological and dermatological care improves patient outcomes and can save costs.

Modern skin cancer treatments can cause skin side effects and hair loss, affecting patients' quality of life.
 August 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The conclusion is that using light-sheet fluorescence microscopy with a special solution can effectively create detailed 3D images of human skin for dermatological research.
 12 citations,
October 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
12 citations,
October 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hormone therapy in transgender women can affect hair growth and acne, and there are specific skin issues related to gender-affirming surgery, but more research is needed on their dermatological health.
 238 citations,
July 2003 in “British Journal of Plastic Surgery”
238 citations,
July 2003 in “British Journal of Plastic Surgery” Hidradenitis suppurativa, a chronic skin disease, can be managed with antibiotics, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery. Early diagnosis and careful planning are key, and laser treatment can be an efficient solution for mild to severe cases.
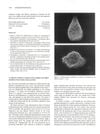 8 citations,
September 1993 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
8 citations,
September 1993 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” A new method helps isolate key hair components to study hair growth and loss.
 2 citations,
September 2013 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
September 2013 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” HIV-positive patients, especially men who have sex with men, had a high rate of skin diseases and sexually transmitted infections.

Higher EULAR/ACR scores in SLE patients predict more organ damage.
 January 2015 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
January 2015 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Topical tacrolimus is effective and safe for treating alopecia areata.
 128 citations,
February 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
128 citations,
February 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata significantly lowers the quality of life, especially in emotional and mental health aspects.






















