 74 citations,
May 2016 in “Current opinion in pediatrics, with evaluated MEDLINE/Current opinion in pediatrics”
74 citations,
May 2016 in “Current opinion in pediatrics, with evaluated MEDLINE/Current opinion in pediatrics” Both vitiligo and alopecia areata involve an immune response triggered by stress and specific genes, with treatments targeting this pathway showing potential.
 4 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
4 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” New treatments targeting T-cell pathways are needed for better alopecia areata management.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document lists various dermatology topics, treatments, and diagnostic methods.
 47 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology”
47 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology” Changes in skin microbes play a role in some skin diseases and could lead to new treatments.
 23 citations,
April 1993 in “Gastroenterology”
23 citations,
April 1993 in “Gastroenterology” A mother and son both had ulcerative colitis and alopecia, suggesting a genetic link in autoimmune disorders and successful treatment with cyclosporine.
 21 citations,
May 2016 in “The Cochrane library”
21 citations,
May 2016 in “The Cochrane library” Topical minoxidil helps treat female pattern hair loss, but more research needed for other treatments.
 11 citations,
November 2021 in “BMJ Open”
11 citations,
November 2021 in “BMJ Open” People with alopecia areata have higher rates of mental health issues, autoimmune diseases, and infections.
 82 citations,
August 2017 in “Cell Reports”
82 citations,
August 2017 in “Cell Reports” An imbalanced gut and lack of biotin can cause hair loss in mice.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” The document is a detailed medical reference on skin and genetic disorders.
 July 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
July 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 45 citations,
April 2019 in “International Immunology”
45 citations,
April 2019 in “International Immunology” The study concluded that immune cells attacking hair follicles cause hair loss in alopecia, with genetics and environment also playing a role, and highlighted the potential of certain treatments.
 4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes”
4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes” Our microbiome may affect the development of the hair loss condition Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed to understand this relationship.
20 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Biologics show promise in treating various stubborn skin diseases, but more research and better reimbursement criteria are needed.
143 citations,
January 2007 in “The American Journal of Human Genetics” Certain genes on chromosomes 6, 10, 16, and 18 may increase the risk of alopecia areata.

Hidradenitis Suppurativa has genetic links, with certain gene mutations more common in patients and a third of cases having a family history.
 68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Shrinking skin cancer increases the chance of cancer in nearby lymph nodes.
 September 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document covers various dermatological conditions and their studies.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology Online Journal” A patient with Crohn's disease grew back their hair after stopping Adalimumab, which had caused hair loss.
 4 citations,
May 1989 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine”
4 citations,
May 1989 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine” Crohn's disease can cause hair loss before other symptoms appear.

The CDC reports 23 measles cases in unvaccinated US kids, new treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis and osteopenia are approved, poor sleep may cause migraines, atopic dermatitis could lead to asthma, migraines might increase Crohn's disease risk, cancer may raise heart disease risk, gout is linked to prostate issues, Cabo Verde is malaria-free, social factors and vitamin D affect dementia risk, smoking increases hair loss risk, certain drugs might lower thyroid disease risk in arthritis, noma is a neglected disease, and meal timing could impact heart health.
 1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Some medications for inflammation can cause a condition with scalp rashes and hair loss, often linked to Crohn's disease, and may require treatment changes to prevent permanent hair loss.
 3 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
3 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Some people with primary cicatricial alopecia also have inflammatory bowel disease, suggesting a possible connection.
9 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology” Infliximab may cause hair loss in Crohn's disease patients.
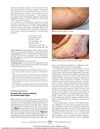 21 citations,
September 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology”
21 citations,
September 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman developed psoriasis after taking certolizumab pegol, improving after stopping the drug and starting other treatments.
 72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Anti-TNF therapy can cause a unique type of hair loss that may get better with topical treatments without stopping the therapy.
 6 citations,
November 2023 in “Clinical Pharmacokinetics”
6 citations,
November 2023 in “Clinical Pharmacokinetics” Ritlecitinib shows promise as a versatile treatment for various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
7 citations,
January 2017 in “Dermatology Online Journal” TNF-inhibitor induced alopecia can be treated effectively with different therapies.
 1 citations,
October 2015 in “The American journal of gastroenterology”
1 citations,
October 2015 in “The American journal of gastroenterology” Stopping infliximab and using strong topical steroids can regrow hair lost due to psoriasiform alopecia.
 December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The meeting highlighted the importance of genetic testing and multidisciplinary approaches in pediatric dermatology.
49 citations,
January 2012 in “Dermatology” Severe anti-TNF-α induced scalp eruptions often need stopping the drug and using systemic therapy to avoid scarring.

























