 126 citations,
April 2015 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
126 citations,
April 2015 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Choosing the right patients, using proper techniques, and having thorough knowledge are key to preventing and managing dermal filler complications.
 19 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
19 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Lupus panniculitis of the scalp causes linear hair loss and needs ongoing treatment to prevent recurrence and lupus.
6 citations,
April 2020 in “Cureus” Platelet-rich plasma injections can effectively treat alopecia areata barbae.
 183 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International”
183 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International” AA-PRP injections effectively increase hair count and thickness for male pattern hair loss.
 5 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
5 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Experts advise using sunscreen and proper skin care before, during, and after procedures to speed healing, prevent complications, and reduce scarring.
 7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stopping imipramine reduced the woman's hair loss.
 March 2018 in “Trends in Immunotherapy”
March 2018 in “Trends in Immunotherapy” Combining triamcinolone acetonide with immunotherapy can help regrow hair in some alopecia totalis patients.
 November 2024 in “Deleted Journal”
November 2024 in “Deleted Journal” Platelet-rich plasma injections can help treat hair loss in lupus patients.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Skin appendage disorders” A combination of methotrexate injections and CO2 laser treatment led to complete hair regrowth in two patients with hard-to-treat alopecia.
21 citations,
May 2017 in “Paediatric drugs” Individualized treatment plans are crucial for children with alopecia areata, with promising options like JAK inhibitors showing significant hair regrowth.
December 2020 in “Aktualʹnì problemi sučasnoï medicini” Combining betamethasone and PRP injections works best for treating alopecia areata.
 4 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair loss treatment caused more hair loss in a man.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document says a skin condition called alopecia areata causes hair loss and stress, and is treated with strong skin creams, injections, or other therapies, but treatment success varies.
 April 2020 in “Trends in Immunotherapy”
April 2020 in “Trends in Immunotherapy” Combining triamcinolone acetonide and immunotherapy can help regrow hair in some alopecia totalis patients.
 May 1993 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
May 1993 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” Formestane is a preferred second-line treatment for advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women because it's effective and has fewer side effects.
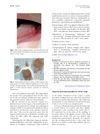 13 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
13 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A rare scalp condition causing hair loss and cysts in young men can be treated effectively with a specific steroid injection.
 5 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” 67 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” 67 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” The document suggests a personalized treatment plan for alopecia areata based on the patient's age and hair loss severity, using a range of therapies ranked by effectiveness and safety.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Candida antigen is an effective and promising treatment for alopecia areata.
 63 citations,
October 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
63 citations,
October 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Red, swollen skin patches are a common allergic reaction to heparin injections, and testing with different heparin types can help find a suitable treatment.
 August 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
August 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Dr. George A. Farber recommends using follicular unit transplantation for hair restoration because it gives a more natural look and has fewer problems compared to the older miniflap technique.
 August 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
August 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Follicular unit hair transplantation is better than Miniflap Hair Restoration due to less scarring and more natural results.
 January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” In 2002, various skin reactions were reported due to different drugs, including allergies, hair loss, skin lesions, and other skin conditions.
 51 citations,
October 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
51 citations,
October 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride increases hair density in female androgenetic alopecia, but individual results may vary.
 152 citations,
March 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
152 citations,
March 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Superficial granulomatous pyoderma is a unique, mild form of skin disease that often heals without strong medication and responds well to milder treatments.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical and medical investigations”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical and medical investigations” Herbal lotions are effective for severe hair loss, with a 64.8% success rate, but relapse is common and long-term management requires allergen control and possible corticosteroid use.
 8 citations,
June 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
8 citations,
June 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Exosomes from umbilical cord cells fix hearing loss and damaged ear hair cells in mice.
 November 2023 in “Dermatologica sinica/Zhōnghuá pífūkē yīxué zázhì”
November 2023 in “Dermatologica sinica/Zhōnghuá pífūkē yīxué zázhì” Upadacitinib helped regrow hair in a severe alopecia areata patient but stopping treatment caused hair loss to return.
 November 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Regenerative medicine is effective and safe for treating vitiligo.
32 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Temporal triangular alopecia is a non-scarring hair loss in children, often linked to other health conditions.























