 118 citations,
September 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
118 citations,
September 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hormones, especially androgens, play a big role in acne, but most acne sufferers don't have a hormone disorder. Hormonal treatments, including birth control pills, can be very effective for women whose acne doesn't improve with regular treatments.
1 citations,
May 2024 in “Pharmaceutics” Hemp is a promising ingredient for skin products due to its healing and soothing properties.
 26 citations,
January 2013 in “BioMed Research International”
26 citations,
January 2013 in “BioMed Research International” Hormonal changes after childbirth and menopause can lead to women's hair loss and facial hair growth, with a need for better treatments.
3 citations,
November 2022 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” The substances improved hair regrowth and protected hair cells in humans and mice.
 7 citations,
June 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
June 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Elderly men with a scalp condition healed in about 26 days using specific creams and dressings, with no return of the condition in 6 months.
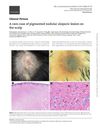
A man had a rare pigmented nodule on his scalp that developed from birthmarks.
139 citations,
October 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The nail matrix has a reduced immune response, protecting it from autoimmunity.
 19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Horizontal scalp biopsy sections are better for diagnosing alopecia areata, showing fewer hair follicles and more miniaturized hairs.
 13 citations,
July 2004 in “Skinmed”
13 citations,
July 2004 in “Skinmed” Common types of non-scarring hair loss have various causes and treatments, but more effective solutions are needed.
 10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine”
10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” The article explains how to identify and treat excessive hair growth in women, which can be distressing and may signal other health problems.
 April 2014 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
April 2014 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Women over forty can maintain skin and hair health with lifestyle and dietary changes.
 February 2024 in “Frontiers in physiology”
February 2024 in “Frontiers in physiology” Hair follicle stem cells help skin heal and grow during stretching.
 688 citations,
June 2007 in “Cell Stem Cell”
688 citations,
June 2007 in “Cell Stem Cell” Removing the ATR gene in adult mice causes rapid aging and stem cell loss.
 43 citations,
July 2019 in “Stem Cells International”
43 citations,
July 2019 in “Stem Cells International” Advancements in creating skin grafts with biomaterials and stem cells are promising, but more research is needed for clinical application.
 August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy”
August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy” Stem-cell therapy shows promise for skin conditions but needs more research.
 138 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics”
138 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics” Protoporphyrin IX is useful in cancer treatment but can cause health problems if not properly regulated.
 54 citations,
November 2015 in “Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology”
54 citations,
November 2015 in “Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology” Keratins are important for skin cell health and their problems can cause diseases.
 68 citations,
March 1965 in “The BMJ”
68 citations,
March 1965 in “The BMJ” Hormones and genetics affect hair growth and patterns, with some changes reversible and others not.
 1 citations,
September 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The meeting highlighted major advances in skin research, including new findings on skin microbes, genetic links to skin diseases, and improved treatments for various conditions.
 January 1998 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
January 1998 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” The document recommends all three dermatology books for a library, noting their detailed content but also suggesting improvements in clarity and consistency.
 3 citations,
December 2022 in “Cells”
3 citations,
December 2022 in “Cells” Cannabinoids like CBD and THC may help treat non-cancer skin diseases, but more research is needed.
 74 citations,
May 2016 in “Current opinion in pediatrics, with evaluated MEDLINE/Current opinion in pediatrics”
74 citations,
May 2016 in “Current opinion in pediatrics, with evaluated MEDLINE/Current opinion in pediatrics” Both vitiligo and alopecia areata involve an immune response triggered by stress and specific genes, with treatments targeting this pathway showing potential.
 72 citations,
April 2008 in “Organogenesis”
72 citations,
April 2008 in “Organogenesis” Wnt signaling is crucial for skin and hair development and its disruption can cause skin tumors.
 30 citations,
July 2017 in “BioEssays”
30 citations,
July 2017 in “BioEssays” Activating NRF2 might help treat hair disorders by improving antioxidant defenses.
 February 2023 in “Molecules”
February 2023 in “Molecules” Cactus extract from Notocactus ottonis may help promote hair growth.
 39 citations,
November 2021 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
39 citations,
November 2021 in “Clinical Endocrinology” Testosterone replacement is recommended for men with low testosterone levels and symptoms of hypogonadism.
 32 citations,
January 2017 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases”
32 citations,
January 2017 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” FOXN1 gene mutations cause a rare, severe immune disease treatable with cell or tissue transplants.
22 citations,
January 2009 in “Advances in experimental medicine and biology” FOXN1 mutations cause severe immunodeficiency, hair loss, nail issues, and thymus defects.
 33 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of clinical immunology”
33 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of clinical immunology” New treatments for immune disorders caused by FOXN1 deficiency are promising.
 17 citations,
June 2017 in “Gene”
17 citations,
June 2017 in “Gene” A rare genetic mutation found in an Indian family can be detected through prenatal screening.

























