 1 citations,
November 2023 in “JAAD case reports”
1 citations,
November 2023 in “JAAD case reports” Mogamulizumab, a skin cancer drug, may cause hair loss similar to alopecia areata.
10 citations,
January 2012 in “Case reports in medicine” Diphencyprone can cause unexpected and possibly permanent vitiligo.
 5 citations,
February 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
5 citations,
February 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Different immune cells like platelets, mast cells, neutrophils, macrophages, T cells, B cells, and innate lymphoid cells all play roles in skin wound healing, but more research is needed due to inconsistent results and the complex nature of the immune response.
 July 2023 in “Stem Cells Translational Medicine”
July 2023 in “Stem Cells Translational Medicine” Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (MSCs) help in wound healing and tissue regeneration, but can also contribute to tumor growth. They show promise in treating chronic wounds and certain burns, but their full healing mechanisms and potential challenges need further exploration.
 119 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine”
119 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine” Rhodococcus equi causes severe pneumonia in young foals, and effective vaccines are needed due to foals' weak immune responses.
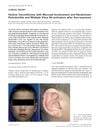 12 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica”
12 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica” Women with early onset androgenetic alopecia have worse lipid profiles.
 9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that fexofenadine reduces inflammation in chronic hives, cholestyramine helps half of pregnant women with itchy rashes, and relaxing incisions are a good alternative in facial surgery for the elderly.
 139 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
139 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Transplant success has improved with better immunosuppressive drugs and donor matching.
 99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology”
99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology” New treatments for Alopecia Areata show promise but need to be more effective and affordable.
 65 citations,
May 2017 in “Advances in wound care”
65 citations,
May 2017 in “Advances in wound care” Toll-like receptors are important for wound healing, but can slow it down in diabetic wounds.
 49 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
49 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia universalis by promoting hair regrowth.
 43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Recognizing the different stages of alopecia areata is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 39 citations,
May 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
39 citations,
May 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The document concludes that treatment for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma should be customized to each patient's disease stage, balancing benefits and side effects, with no cure but many patients living long lives.
 37 citations,
September 2008 in “The American journal of surgical pathology”
37 citations,
September 2008 in “The American journal of surgical pathology” Hair follicle hyperplasia is common in both benign and malignant skin lymphoproliferative disorders, with a proposed new term "pseudolymphomatous adnexitis."
 32 citations,
January 2017 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases”
32 citations,
January 2017 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” FOXN1 gene mutations cause a rare, severe immune disease treatable with cell or tissue transplants.
 23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease affecting hair follicles, influenced by genetic and environmental factors, with rodent models being essential for research.
 21 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of molecular medicine”
21 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of molecular medicine” FoxN1 gene is essential for proper thymus structure and preventing hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 1996 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy”
3 citations,
January 1996 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy” Zidovudine may cause hair loss in advanced-stage HIV patients.
 2 citations,
May 2019 in “Advances in wound care”
2 citations,
May 2019 in “Advances in wound care” Blood-derived CD34+ cells speed up healing, reduce scarring, and regrow hair in skin wounds.
 2 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
2 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” RANKL improves the immune response against herpes simplex virus by enhancing T cell activation and could help develop better treatments or vaccines.
 1 citations,
March 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy”
1 citations,
March 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy” NF-κB signaling is crucial in many diseases and can be targeted for new treatments.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 August 2022 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
August 2022 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Propylthiouracil can cause hair loss, reduced sweating, and nail issues, but stopping the drug can reverse hair and nail problems.

The document tests knowledge and decision-making in hematology through multiple-choice questions.

The document provides 70 multiple choice questions to improve haematology skills.
 316 citations,
June 2017 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
316 citations,
June 2017 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Fat tissue-derived cells show promise for repairing body tissues, but more research and regulation are needed for safe use.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
 130 citations,
November 2017 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
130 citations,
November 2017 in “Frontiers in Immunology” The conclusion is that Treg-targeted therapies have potential, but more knowledge of Treg biology is needed for effective treatments, including for cancer.
 85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition often starting before age 20, with varied treatment success and a need for personalized treatment plans.
 70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Topical drugs and near-infrared light therapy show potential for treating alopecia.





























