 23 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
23 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia's cause is unclear, affects mainly postmenopausal women, and current treatments focus on stopping hair loss rather than regrowth.
 3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair loss is complex, affects many people, has limited treatments, and requires more research on its causes and psychological impact.
 11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Skin reactions to drugs are common and can be deadly, usually requiring stopping the drug and may be better prevented with genetic testing in the future.
 September 2023 in “Fides et Ratio”
September 2023 in “Fides et Ratio” The safety and effectiveness of gender-affirming treatments for children are uncertain, with potential long-term risks like infertility.
 77 citations,
June 2015 in “Nature Reviews Urology”
77 citations,
June 2015 in “Nature Reviews Urology” Some common medications can harm male fertility, but many effects can be reversed.
 38 citations,
November 2000 in “Hastings Center Report”
38 citations,
November 2000 in “Hastings Center Report” The document suggests medicine should integrate biological and cultural factors and focus on holistic, equitable care.
7 citations,
August 2019 in “JAAD Case Reports” Hidradenitis suppurativa may be more severe in people with Mediterranean fever gene mutations.
 89 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology”
89 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology” The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is important for tissue development and has potential in regenerative medicine, but requires more research for therapeutic use.
 31 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
31 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Hair becomes gray and thin as we age, and while most hair loss in older people is due to genetics, there's a chance for gray hair to regain color under certain conditions.
 October 2024 in “Journal of Education Health and Sport”
October 2024 in “Journal of Education Health and Sport” Alopecia areata treatment should be personalized, using topical or systemic therapies based on severity, with promising options like JAK inhibitors needing more research.
 May 2024 in “Journal of Education, Health and Sport”
May 2024 in “Journal of Education, Health and Sport” Current treatments for folliculitis decalvans include antibiotics, isotretinoin, and potential new therapies like botulinum toxin A and PRP.
Biomimetic dermal papilla spheres can help regenerate hair to some extent.
 76 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
76 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Dermal Papilla cells are a promising tool for evaluating hair growth treatments.
 40 citations,
January 2009 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
40 citations,
January 2009 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Fetal cells could improve skin repair with minimal scarring and are a potential ready-to-use solution for tissue engineering.
 35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that there are various treatments for different types of alopecia, but more research is needed for evidence-based treatments.
 12 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
12 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Some patients on immunosuppressants had a weaker immune response to the Sinovac-CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine.
 9 citations,
March 2013 in “Expert opinion on biological therapy”
9 citations,
March 2013 in “Expert opinion on biological therapy” Epidermal stem cells have potential for personalized regenerative medicine but need careful handling to avoid cancer.
 June 2023 in “JMIR dermatology”
June 2023 in “JMIR dermatology” The conclusion is that recognizing the difference between gender identity and biological sex is crucial in dermatology to improve patient care and research accuracy.
 6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of regenerative medicine & tissue engineering”
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of regenerative medicine & tissue engineering” The review concludes that innovations in regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and developmental biology are essential for effective tissue repair and organ transplants.
 47 citations,
May 2012 in “Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Developmental Biology”
47 citations,
May 2012 in “Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Developmental Biology” The conclusion is that understanding how feathers and hairs pattern can help in developing hair regeneration treatments.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of biological sciences”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of biological sciences” Gray hair can potentially be reversed, leading to new treatments.
 66 citations,
May 2012 in “Scientific Reports”
66 citations,
May 2012 in “Scientific Reports” Scientists successfully created and transplanted bioengineered hair follicles that function like natural ones, suggesting a new treatment for hair loss.
 3 citations,
September 2023 in “Skin research and technology”
3 citations,
September 2023 in “Skin research and technology” New treatments for skin damage from UV light using stem cells and their secretions show promise for skin repair without major risks.
 25 citations,
April 2021 in “npj Regenerative Medicine”
25 citations,
April 2021 in “npj Regenerative Medicine” Mathematical modeling can improve regenerative medicine by predicting biological processes and optimizing therapy development.
 August 2024 in “International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology”
August 2024 in “International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology” Secretome-based therapies could improve hair growth better than current treatments.
 August 2015 in “Free Radical Biology and Medicine”
August 2015 in “Free Radical Biology and Medicine” The document concludes that the discussed biological mechanisms and potential therapies are not related to hair loss or hair growth.
 December 2022 in “International journal of drug regulatory affairs”
December 2022 in “International journal of drug regulatory affairs” The US and EU lead in cell and gene therapy regulations with more approvals and clinical trials, while India is in early stages with fewer approvals and expedited processes.
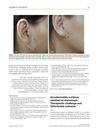 6 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
6 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A man with Acrodermatitis continua did not get better with etanercept treatment, and his condition worsened, suggesting treatment effectiveness may vary by genetics and race.
 4 citations,
March 2013 in “InTech eBooks”
4 citations,
March 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) is a useful tool for studying how drugs interact with skin and diagnosing skin disorders, despite some limitations.
 15 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association”
15 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association” Adalimumab helped control a child's severe eye disease when other treatments failed.




























