 9 citations,
January 2022 in “Theranostics”
9 citations,
January 2022 in “Theranostics” Collagen XVII is important for skin aging and wound healing.
 2 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
2 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped over half of the patients with severe hair loss regrow at least 50% of their hair.
1 citations,
December 2020 in “Case reports in dermatological medicine” A patient with pemphigus vulgaris improved significantly after treatment for an additional viral skin infection.
 March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies”
March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies” The 2006 editorial concluded that immunotherapy was advancing with new drugs, focusing on specific biological therapies and convenient oral treatments, and highlighted the importance of partnerships and new regulations in the field.
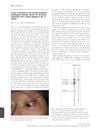 7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A woman with a rare autoimmune disorder had a blister on her eye and unique immune reaction, which was effectively treated with medication.
 13 citations,
January 2018 in “BioMed Research International”
13 citations,
January 2018 in “BioMed Research International” Scalp involvement is common in pemphigus and can lead to hair loss, with the severity of scalp lesions linked to overall disease severity.
21 citations,
December 2014 in “Clinics in dermatology” Squaric acid dibutylester effectively treats alopecia areata.
 124 citations,
October 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
124 citations,
October 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Janus kinase inhibitors are promising treatments for autoimmune skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis.
 24 citations,
March 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
24 citations,
March 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Treg dysfunction is linked to various autoimmune skin diseases, and understanding Treg properties is key for new treatments.
50 citations,
May 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” Certain immune cells contribute to skin autoimmune diseases, and some treatments can reverse hair loss in these conditions.
 129 citations,
November 2005 in “Internal Medicine Journal”
129 citations,
November 2005 in “Internal Medicine Journal” Early detection and intensive treatment of diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus toxins are crucial for reducing severe health effects.
 2 citations,
January 2019
2 citations,
January 2019 The document concludes that autoimmune skin disorders are treated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.
 6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association”
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association” A 7-year-old dog with a rare autoimmune disease was euthanized due to severe anemia and poor prognosis.
 10 citations,
January 2012 in “Lupus”
10 citations,
January 2012 in “Lupus” NEMO syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus are linked in a new disease association.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS cell and tissue engineering”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS cell and tissue engineering” Mesenchymal stem cells show promise for treating various skin conditions and may help regenerate hair.
 13 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
13 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Gamma delta T cells in the skin help with healing and defense but can also cause autoimmune issues, and more research is needed to understand how they are activated.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Herpes gestationis is linked to certain antigens, atopic eczema affects T cell populations and may be eased by breastfeeding, higher doses of anti-androgen treatment can improve androgenic alopecia, topical minoxidil increases hair thickness, long-term methotrexate therapy can cause liver fibrosis in psoriasis patients, and Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus patients aren't at higher risk for autoimmune disorders.
 42 citations,
January 1998 in “BioDrugs”
42 citations,
January 1998 in “BioDrugs” Azathioprine's effectiveness and safety require careful monitoring and more research, especially regarding its use with corticosteroids and the role of TPMT status in patients.
 25 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
25 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Methotrexate effectively treated a 2-year-old's generalized pustular psoriasis without side effects.

No treatment alters the natural progression of alopecia areata, and effectiveness varies, with some possibly working better in children.
 41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design”
41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design” Current and future treatments for alopecia areata focus on immunosuppression, immunomodulation, and protecting hair follicles.
 1 citations,
February 2023 in “Deleted Journal”
1 citations,
February 2023 in “Deleted Journal” Diphenylcyclopropenone is effective for treating alopecia areata but has a high relapse rate.
 February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences”
February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences” No cure exists for alopecia areata, and treatments are personalized.
 49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Despite progress in treatment, the exact cause of Alopecia areata is still unknown.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cell reconstitution after thymus transplantation can cause hair whitening and loss.
 7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that various childhood hair and nail disorders exist, some may improve on their own, and advances in genetics and immunology could enhance treatment and counseling.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Targeted therapies for lung cancer are effective but require careful management of side effects to benefit patients.
 1 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” Melanocytes produce melanin; their defects cause vitiligo and hair graying, with treatments available for vitiligo.



























