 1 citations,
February 2023 in “Deleted Journal”
1 citations,
February 2023 in “Deleted Journal” Diphenylcyclopropenone is effective for treating alopecia areata but has a high relapse rate.
December 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology” Most patients with small patches of hair loss usually regrow hair.
 13 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
13 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Cyclosporine combined with corticosteroids is more effective for severe alopecia areata than cyclosporine alone.
14 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” Vitamin D might be involved in the development of alopecia areata and could help in its treatment.
 8 citations,
October 1989 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
October 1989 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A 5-year-old boy's seasonal hair loss is linked to his allergies.
 April 2024 in “Liječnički vjesnik”
April 2024 in “Liječnički vjesnik” Modern treatments can effectively regrow hair and improve life for people with alopecia areata.
 January 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib helped most teenagers with severe hair loss regrow hair and had mild side effects.
 1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Certain genes are linked to the risk of developing Alopecia Areata.
February 2017 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Botulinum toxin type A did not help regrow hair in severe alopecia cases.
 3 citations,
April 2021 in “Cureus”
3 citations,
April 2021 in “Cureus” Low Vitamin D is common in people with Alopecia Areata, but its impact on the condition needs more research.
 August 2023 in “JAAD international”
August 2023 in “JAAD international” Pediatric dermatologists have varied preferences for treating alopecia areata in children, with no standard FDA-approved treatments and some using JAK inhibitors despite risks.
 1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman's complete hair loss condition improved after recovering from COVID-19.
18 citations,
January 2013 in “PLoS ONE” HLA-DRB5 and other genes may be linked to alopecia universalis.
 14 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
14 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Scalp Roller therapy helped improve hair growth in patients with hard-to-treat alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” JAK inhibitors are more effective and safer for treating alopecia areata than dupilumab and apremilast.
 November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Tofacitinib is effective and has minor, reversible side effects for treating severe hair loss in Iran.
 December 2023 in “Journal of dermatology”
December 2023 in “Journal of dermatology” Adults and adolescents with severe alopecia areata are willing to take significant health risks for a better chance of hair regrowth.
 April 2023 in “Revista colombiana de reumatología”
April 2023 in “Revista colombiana de reumatología” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib can effectively treat severe alopecia areata.
3 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association /Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association” General practitioners in Qassim have satisfactory knowledge of alopecia areata but need more education to address gaps and misconceptions.
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Certain drugs can cause hair loss, but stopping the drug usually leads to hair regrowth.
 November 2023 in “PubMed”
November 2023 in “PubMed” Pentoxifylline is a safe and effective alternative to triamcinolone acetonide for treating localized alopecia areata.
 8 citations,
July 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
8 citations,
July 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” A man's scalp condition was misidentified as hair loss dots but was actually a common follicular disorder.
 August 2021 in “Revista Colombiana de Reumatología/Revista Colombiana de Reumatologia”
August 2021 in “Revista Colombiana de Reumatología/Revista Colombiana de Reumatologia” Janus kinase inhibitors may effectively treat severe alopecia areata unresponsive to other treatments.
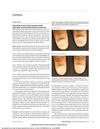 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” There's no strong link between Alopecia Areata, a hair loss condition, and fatty liver, but more research is needed.
22 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Ruxolitinib helped a man regrow his beard after years of hair loss.
110 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Alopecia areata is a genetic and immune-related hair loss condition that is often associated with other autoimmune diseases and does not typically cause permanent damage to hair follicles.
1 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Botulinum toxin A injections may help treat difficult cases of total hair loss.
33 citations,
October 2013 in “Cutaneous and ocular toxicology” Oral cyclosporine can help regrow hair in severe alopecia areata cases.
 June 2019 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
June 2019 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Dermoscopy is useful for tracking alopecia areata treatment, with yellow dots and new vellus hairs being good indicators of hair regrowth.




















