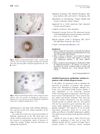
Overview of Alopecia Areata
TLDR Alopecia areata is a genetic and immune-related hair loss condition that is often associated with other autoimmune diseases and does not typically cause permanent damage to hair follicles.
Alopecia areata was a genetic, immune-mediated disease causing hair loss in both children and adults, often linked with conditions like asthma and thyroid disease. Affecting 6-7 million people in the U.S., it did not permanently damage hair follicles, allowing for potential regrowth. Genetic studies identified several loci related to immune system functions. Despite various treatments, there was no cure, prompting exploration of new therapies targeting immune pathways and neuropeptide functions. The National Alopecia Areata Foundation initiated programs to accelerate treatment development.