 59 citations,
November 2015 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
59 citations,
November 2015 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Oxidative stress damages hair and contributes to aging, and managing it can help maintain hair health.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin cells and certain hair follicle areas produce hemoglobin, which may help protect against oxidative stress like UV damage.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Apocynin may protect skin cells from aging and damage caused by UVB light.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Honey mixture improved damaged Asian hair, making it stronger, softer, and shinier.
 15 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
15 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hair aging and loss are caused by genetics, hormones, environment, and grooming, with treatments like minoxidil effective for certain types of hair loss.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Compounds A and B help men's skin recover faster by reducing oxidative damage and increasing energy levels.
 74 citations,
March 2001 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
74 citations,
March 2001 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that skin biopsies, genetic and environmental factors, and specific treatments are important in managing cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
 January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A child with trichothiodystrophy also had autoimmune thyroiditis and anemia, which is a new finding.
 11 citations,
April 2013 in “SpringerPlus”
11 citations,
April 2013 in “SpringerPlus” Human skin's melanocytes respond to light by changing shape, producing pigments and hormones, which may affect sleep patterns.
 November 2011 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
November 2011 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Environmental, chemical, mechanical, and personal health factors can all damage hair and contribute to hair loss or changes in hair quality.
 41 citations,
October 2000 in “Dermatologic clinics”
41 citations,
October 2000 in “Dermatologic clinics” Better hair care products are needed to protect against grooming and chemical damage.

Different stem cells are key for hair growth and health, and understanding their regulation could help treat hair loss.
 19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The study found that long-term sun exposure does not significantly affect follicular plugs on the scalp, and the scalp's appearance is unique compared to other body parts.
 September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” People with advanced chronic kidney disease often have skin problems, which can be treated with various medications and procedures to improve their quality of life.
 22 citations,
July 2004 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
22 citations,
July 2004 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” UV radiation and visible light can damage hair, but there are ways to protect it.
4 citations,
June 2016 in “PubMed” Repeated dyeing and shampooing cause hair color loss and damage.
 January 2021 in “Journal of clinical and cosmetic dermatology”
January 2021 in “Journal of clinical and cosmetic dermatology” Human skin responds to light with protective mechanisms, but more research is needed to understand these processes and their implications for health and therapy.
 8 citations,
March 2018 in “Cosmetics”
8 citations,
March 2018 in “Cosmetics” UV radiation damages hair by creating holes and peeling cuticle layers.
 20 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
20 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Germany recognizes skin cancer from UV exposure as an occupational disease, emphasizing prevention and care for affected workers.
 4 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
4 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Aging causes hair loss and graying due to stem cell decline and changes in cell behavior and communication.
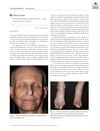 March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Rothmund-Thomson syndrome type 2 can cause chronic, poorly healing wounds.
 19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Anti-cancer treatments can cause reversible hair loss, skin sensitivity, pigmentation changes, nail damage, and skin reactions, with a need for more research on managing these side effects.
 1 citations,
December 2005 in “Therapeutische Umschau”
1 citations,
December 2005 in “Therapeutische Umschau” The document concludes that protecting skin from the sun, avoiding smoking, and using treatments like Minoxidil and Finasteride can help manage skin and hair aging.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “Frontiers in veterinary science”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “Frontiers in veterinary science” Activating autophagy in dogs with certain diseases improves their skin and hair.
62 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of Human Evolution/Journal of human evolution” Forensic DNA Phenotyping can help predict physical traits from crime scene DNA to identify suspects.

Skin changes throughout life, from development before birth to aging effects like wrinkles, influenced by both genetics and environment.
 36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials”
36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials” A new skin-whitening agent using a peptide from wheat is safe and effective at reducing skin pigmentation.
 23 citations,
August 2019 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
23 citations,
August 2019 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Pollution exposure speeds up hair damage.
 10 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of skin cancer”
10 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of skin cancer” PKC ε increases hair follicle stem cell turnover and may raise skin cancer risk.
 2 citations,
March 2014 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
2 citations,
March 2014 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The editor suggests removing "race" and "ethnicity" from dermatology and creating tools to objectively assess skin color and hair texture.




























