51 citations,
January 2007 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Scientists discovered a unique hair protein, KAP24.1, with a special structure, found only in the upper part of hair cuticles.
 182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine”
182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine” The PDGF/PDGFR pathway is a potential drug target with mixed success in treating various diseases, including some cancers and fibrosis.
 25 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
25 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Many patients on new leukemia drugs had mild to moderate skin reactions.
 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Science Translational Medicine”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Science Translational Medicine” Blocking a certain signal in the gp130 receptor can improve tissue healing and lessen osteoarthritis symptoms.
 January 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
January 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The gp130 receptor helps in tissue regeneration and disease progression, and manipulating it could improve healing and prevent disease.
 215 citations,
March 2011 in “Clinical Cancer Research”
215 citations,
March 2011 in “Clinical Cancer Research” Sorafenib is effective in treating Desmoid Tumor/Deep Fibromatosis.
1 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of dermatological science” Combining ficlatuzumab and gefitinib can cause severe scarring hair loss.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Androgens increase growth factors in skin cells, which may lead to acne.
 October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Excessive eyelash growth from erlotinib may indicate positive tumor response and help treat madarosis.

mEphA1 receptor tyrosine kinase is important for skin and hair development and may play a role in certain diseases.
88 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Tyrosine kinases are important in skin autoimmune diseases and could be targets for new treatments.
 6 citations,
November 2023 in “Clinical Pharmacokinetics”
6 citations,
November 2023 in “Clinical Pharmacokinetics” Ritlecitinib shows promise as a versatile treatment for various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Indian Journal of Pharmacology” Nilotinib can cause generalized keratosis pilaris.
 7 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A woman's hair turned gray and fell out after starting a cancer drug called imatinib mesylate.
 16 citations,
March 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
16 citations,
March 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” A cancer drug called nilotinib might cause hair loss due to inflammation around hair follicles.
 2 citations,
March 2023 in “BMC ecology and evolution”
2 citations,
March 2023 in “BMC ecology and evolution” Some hair protein genes evolved early and were adapted for use in hair follicles.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology Online Journal” An 84-year-old man developed a rare scalp condition from a cancer drug but continued treatment as it was otherwise well tolerated.
 7 citations,
May 2014 in “Clinical practice”
7 citations,
May 2014 in “Clinical practice” Cooling the scalp may prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, hair often grows back after treatment, and nail issues usually improve after stopping the drug.
 263 citations,
February 2013 in “Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology”
263 citations,
February 2013 in “Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology” Polymeric nanoparticles show promise for treating skin diseases.
 1 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of dermatology and dermatitis”
1 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of dermatology and dermatitis” Tyrosine kinase inhibitors show promise in treating some skin diseases but their definitive role in dermatology is still unclear.
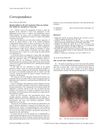 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
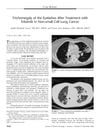 12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology”
12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology” A cancer patient's eyelashes grew excessively without other common side effects after taking the cancer drug erlotinib.
 7 citations,
May 2022 in “PLOS ONE”
7 citations,
May 2022 in “PLOS ONE” Certain genes and pathways are linked to the production of finer and denser wool in Hetian sheep.
 June 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
June 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Protein tyrosine kinases are key in male pattern baldness, affecting skin structure, hair growth, and immune responses.
 March 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Immune changes and specific genes contribute to male hair loss.
4 citations,
December 2020 in “Natural Product Sciences” The method identified and measured ten compounds from Eclipta prostrata, showing significant enzyme inhibitory effects.
 65 citations,
February 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
65 citations,
February 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Anti-acne medications may work by reducing the activity of a protein involved in acne development.
 58 citations,
March 2020 in “Scientific Reports”
58 citations,
March 2020 in “Scientific Reports” EGFR-TKIs can cause significant skin, nail, and organ side effects.
100 citations,
December 2002 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” Researchers mapped and categorized specific keratin-associated protein genes on human chromosome 21q22.1.
 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Physical chemistry chemical physics/PCCP. Physical chemistry chemical physics”
16 citations,
January 2017 in “Physical chemistry chemical physics/PCCP. Physical chemistry chemical physics” The 3D structure of a key hair protein was modeled, revealing specific helical structures and stabilization features.























