20 citations,
March 1975 in “Journal of steroid biochemistry/Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” The study concludes that a genetic mutation in TFM mice leads to reduced androgen receptor activity, affecting the body's response to male hormones.
 12 citations,
March 2018 in “Medicine”
12 citations,
March 2018 in “Medicine” A postmenopausal woman's hirsutism and high testosterone levels improved after surgery for an ovarian tumor not seen on ultrasound.
 12 citations,
May 2005 in “Current obstetrics and gynaecology/Current obstetrics & gynaecology”
12 citations,
May 2005 in “Current obstetrics and gynaecology/Current obstetrics & gynaecology” Hirsutism is too much hair growth in women like the pattern in men, often caused by high male hormones, and can be treated with hormone control and hair removal methods.
[object Object]  9 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
9 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” About 19.4% of Iranian women in the study have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, with the most common type involving irregular periods and high male hormone levels, but their heart and metabolic health is similar to women without the condition.
 5 citations,
January 2014 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
5 citations,
January 2014 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Hormonal treatments like birth control pills can improve acne in women with excess hair growth and hormone imbalances.
 5 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Female pattern hair loss diagnosis is challenging and should use dermoscopy and histopathology instead of pattern recognition, as hormones may not always be the cause.
 3 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
3 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Skin problems in patients with polycystic ovarian disease are linked to body weight, blood sugar, and hormone levels.
 3 citations,
September 2016 in “Natural Product Communications”
3 citations,
September 2016 in “Natural Product Communications” Germacrene analogs, especially 8-Hydroxy germacrene B, are more effective than germacrone at blocking a hormone-related enzyme and could help treat hair loss.
 1 citations,
May 2019 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
1 citations,
May 2019 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” Spironolactone may cause sexual pain and arousal issues in women, which can improve after stopping the drug and using hormone cream.
January 2022 in “Journal of Morphological Sciences” A woman's rare ovarian tumor was treated with surgery, which stopped her symptoms and normalized her hormone levels.
 April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's severe male-like symptoms were caused by a rare, benign tumor in her ovary that produced male hormones.
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Female pattern hair loss severity is linked to physical signs of high androgens, not blood hormone levels.
 45 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
45 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical Endocrinology” Testosterone therapy is generally safe for transmen, improves sexual function, and has manageable health risks with proper monitoring.
29 citations,
November 1975 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism” Testosterone is made by Leydig cells, is active when not bound to proteins, and works by binding to receptors in muscles and other tissues.
22 citations,
January 2019 in “Climacteric” Oophorectomy lowers testosterone and estrogen levels in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, with postmenopausal women still producing significant testosterone.
 12 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
12 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Testosterone significantly affects sexual desire in both men and women, but its impact on women is more complex and influenced by psychological factors.
 1 citations,
December 2022 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” The most common skin issues in females with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are excessive hair growth, hair loss, oily skin, acne, dark skin patches, and skin tags, which may be linked to hormone and insulin levels.
 June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Lower adrenal hormone levels may cause hair loss in postmenopausal women, certain patterns help diagnose nail cancer, and a gene variant linked to higher skin cancer risk in kidney transplant patients suggests monitoring folate levels.
[object Object]  July 2022 in “L Endocrinologo”
July 2022 in “L Endocrinologo” A 77-year-old woman with hair loss had high testosterone and 17OH-progesterone levels, but no significant findings on imaging.
88 citations,
September 2003 in “Clinical endocrinology” Hormone treatment for transsexual individuals is effective but carries risks like thromboembolic events and mood changes, with most side effects being minor and reversible.
 16 citations,
January 2000 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism”
16 citations,
January 2000 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism” Antiandrogen drugs can reduce PSA levels in women with excess hair, suggesting PSA is a sign of male hormone activity in women.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Autism's genetics are linked with early age of puberty and less hair loss, but not with hormone levels or polycystic ovary syndrome.
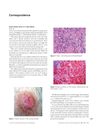 October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology” An 86-year-old man with prostate cancer was diagnosed with a rare, low-grade breast cancer and underwent surgery but declined additional hormone therapy.
 18 citations,
March 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
18 citations,
March 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Estrogen increases blood vessel growth factor production, while testosterone blocks this increase.
Finasteride treats hair loss and prostate issues by lowering certain hormone levels.
 12 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry”
12 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” The new compounds moderately block a specific enzyme and strongly counteract a male hormone, suggesting potential for treating certain male-related health conditions.
 298 citations,
July 2000 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
298 citations,
July 2000 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” About 6.5% of young Caucasian women in Spain have polycystic ovary syndrome.
 77 citations,
March 2004 in “Human Reproduction”
77 citations,
March 2004 in “Human Reproduction” Women with irregular periods and/or excessive body hair are more likely to have polycystic ovaries, and this condition is linked to higher health risks.
 64 citations,
January 2009 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
64 citations,
January 2009 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Myo-inositol helps improve skin conditions and metabolic profiles in young women with PCOS.
 43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Antiandrogen therapy helped increase hair growth in women with hormonal imbalances related to baldness.























