 June 2018 in “Reactions Weekly”
June 2018 in “Reactions Weekly” A 65-year-old man developed a serious skin cancer linked to a drug he was taking for a fungal infection after a bone marrow transplant.
 April 2016 in “JAMA Dermatology”
April 2016 in “JAMA Dermatology” Acne is not a key diagnostic feature for PCOS, postadolescent men with acne may have insulin resistance, melanoma patients often have few moles, tumor size in CSCC indicates higher risk of serious outcomes, and hidradenitis suppurativa is linked to higher risk of heart problems and death.
 October 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
October 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Collagen VII helps skin heal and stay strong, sirolimus may lower skin cancer risk in kidney transplant patients, high-molecular-mass hyaluronan helps naked mole rats resist cancer, dermal γδ T cells aid in hair growth in rodents, and overexpression of IL-33 in mouse skin causes itchiness, offering a model for studying allergic inflammation treatments.
10 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of cutaneous medicine and surgery” Patients on dabrafenib and trametinib for melanoma often experience skin side effects.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin cells and certain hair follicle areas produce hemoglobin, which may help protect against oxidative stress like UV damage.
62 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of pathology” Keratin 17 is linked to various diseases, including cancer and skin conditions, and may be a target for diagnosis and treatment.
 24 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman with cervical cancer had rare scalp metastasis causing a unique type of hair loss.
 12 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A cancer drug caused unusual hair growth on a 100-year-old man's scalp and eyelashes.
 8 citations,
September 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
8 citations,
September 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Enlarged sweat gland ducts may indicate scarring hair loss.
1 citations,
October 2007 in “The Cancer Handbook” The document discussed the three most common types of skin cancer: malignant melanoma, basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Malignant melanoma, originating from melanocytes, was noted as the most lethal. BCC, the most common cancer, was debated to potentially arise from hair follicle keratinocytes and was associated with mutations in the sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway, suggesting a link to failed organogenesis. SCC, also arising from keratinocytes, was described as more aggressive than BCC, with the potential to form lethal metastases, unlike BCC, which rarely metastasizes. The document also covered the use of in vivo and in vitro models for studying these skin cancers.
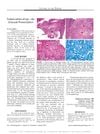
 December 2023 in “Archives of iranian medicine”
December 2023 in “Archives of iranian medicine” Higher iron levels in hair may increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that ERBB2 mutations are common in extramammary Paget disease and may respond to systemic treatments like cancer immunotherapy.
 August 1993 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
August 1993 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Testosterone metabolism in balding scalp cells may not be the main cause of hair loss.
266 citations,
January 2016 in “Development” The study demonstrated that YAP and TAZ proteins were crucial for skin homeostasis, particularly in the basal layer of the skin, where they were found in the nucleus and increased during wound healing. Deleting YAP and TAZ in the skin of adult mice resulted in slower cell proliferation, hair loss, and impaired wound regeneration. The nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ was regulated by Integrin-Src signaling, which was influenced by contact with the basal extracellular matrix. This mechanism was also observed in other squamous epithelia and squamous cell carcinomas. In contrast, columnar epithelia used a different mechanism involving Hippo signaling to keep YAP/TAZ in the cytoplasm. However, when columnar epithelial tumors lost their apical domain, YAP/TAZ became nuclear, making the tumors sensitive to the Src inhibitor Dasatinib.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 66 citations,
April 1995 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology”
66 citations,
April 1995 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” A new protein was made to detect specific skin cell growth receptors and worked in normal skin but not in skin cancer cells.
63 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Runx1 affects hair growth, cancer development, and autoimmune diseases in epithelial tissues.
 21 citations,
May 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
21 citations,
May 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The first in-prison dermatology clinic in the U.S. faced challenges and found certain skin conditions common among inmates, with rare cases of serious skin cancer.
 16 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical Cancer Research”
16 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical Cancer Research” The document concludes that side effects from Smoothened inhibitor drugs for skin cancer are reversible and can be managed with a team approach to maintain quality of life.
13 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in oncology” Reflectance confocal microscopy reliably identifies skin cancer features like horizontal skin tissue sections.

Inhibiting AP-1 changes skin tumor types and affects tumor cell identity.
 February 2023 in “Mağallaẗ Tikrīt li-l-ʻulūm al-ṣirfaẗ/Tikrit journal of pure science”
February 2023 in “Mağallaẗ Tikrīt li-l-ʻulūm al-ṣirfaẗ/Tikrit journal of pure science” Horse skin has a layered epidermis, a dermis with hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands, and is supplied by small arteries.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Higher levels of nidogen1 and type IV collagen are found in basal cell carcinoma compared to normal skin.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus has different forms, is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, and can be treated with various medications, but more targeted therapies are needed.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” SOX4 is crucial for the development of melanoma.
 January 2015 in “Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Dermatology”
January 2015 in “Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Dermatology” Peripilar keratin casts are a helpful sign for diagnosing traction alopecia.
 August 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New hair regrowth model introduced, imiquimod kills skin cancer cells, T-cadherin loss makes skin cancer more invasive, no strong link between PTCH1 gene and skin cancer after transplant, and male teens more likely to have hereditary hair loss.
 April 2005 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery”
April 2005 in “Clinics in Plastic Surgery” Various surgical techniques effectively treat skin diseases and cosmetic issues.
 September 1994 in “Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery”
September 1994 in “Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery” Several doctors received research grants, new workshops and conferences were announced, and new officers were elected.
 February 1990 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 1990 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” New skin treatments in 1987-1988 showed effectiveness for various conditions, but some had side effects or risks.























