 16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ruxolitinib may help treat hair loss by reducing inflammation, promoting hair growth signals, and protecting hair follicle immunity.
[object Object] January 2019 in “프로그램북(구 초록집)” Both tofacitinib and ruxolitinib are effective and tolerable for treating alopecia areata.
January 2018 in “Figshare” Ruxolitinib and tofacitinib are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 January 2016 in “Chemistry & Industry”
January 2016 in “Chemistry & Industry” Two drugs, tofacitinib and ruxolitinib, may help regrow hair by activating hair follicles.
701 citations,
August 2014 in “Nature medicine” Alopecia areata can be reversed by JAK inhibitors, promoting hair regrowth.
50 citations,
May 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” Certain immune cells contribute to skin autoimmune diseases, and some treatments can reverse hair loss in these conditions.
 49 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
49 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia universalis by promoting hair regrowth.
 30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” New treatments targeting immune pathways show promise for severe hair loss but need more research for safety and effectiveness.
21 citations,
May 2017 in “Paediatric drugs” Individualized treatment plans are crucial for children with alopecia areata, with promising options like JAK inhibitors showing significant hair regrowth.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Stopping JAK inhibitor treatment for hair loss can lead to worse hair loss than before the treatment.
 11 citations,
April 2015 in “EBioMedicine”
11 citations,
April 2015 in “EBioMedicine” JAK inhibitors may help treat Alopecia Areata but need careful monitoring due to side effects.
8 citations,
January 2017 in “Dermatology online journal” Tofacitinib helped psoriasis but not alopecia universalis, needing more research.
 6 citations,
March 2016 in “Scandinavian journal of immunology”
6 citations,
March 2016 in “Scandinavian journal of immunology” Janus kinase inhibitors show promise in treating alopecia areata but need more safety research.
4 citations,
January 2020 in “PubMed” JAK inhibitors may become the first approved treatment for alopecia areata if they are proven safe and effective.
 3 citations,
April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Curcumin applied to the skin can start hair growth in mice.
 1 citations,
January 2020 in “Surgical & Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Surgical & Cosmetic Dermatology” Combining oral minoxidil with JAK inhibitors helps regrow hair in severe alopecia areata cases.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study developed a mouse model for Alopecia Areata that responds to treatment, useful for future research.
 October 2023 in “International journal of rheumatic diseases”
October 2023 in “International journal of rheumatic diseases” New treatments targeting the JAK signaling pathway, especially JAK inhibitors, show promise for alopecia areata.
 September 2022 in “Hair transplant forum international”
September 2022 in “Hair transplant forum international” JAK inhibitors like baricitinib are a new FDA-approved treatment for alopecia areata, but safety data is incomplete.
December 2017 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” JAK inhibitors show promise for treating Alopecia Areata, while statins are not recommended.
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Researchers found three different ways drugs work to treat hair loss from alopecia areata and identified key factors for personalized treatment.
March 2017 in “Current dermatology reports” Topical JAK inhibitors can effectively treat alopecia areata and vitiligo by modulating immune responses.
 February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata by reversing hair loss.
 September 2014 in “SciBX”
September 2014 in “SciBX” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata and promote hair regrowth.
 49 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib caused significant hair regrowth in adolescents with alopecia universalis who didn't respond to other treatments.
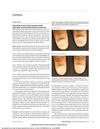 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 28 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
28 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Tofacitinib shows promise for treating severe hair loss in adults and teens, with many experiencing regrowth, but hair loss returns when treatment stops.
 20 citations,
January 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
20 citations,
January 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Recent advances in hair loss treatments show significant progress.
[object Object]  7 citations,
March 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
7 citations,
March 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Several new treatments for different types of hair loss show promise in improving patient quality of life.
 139 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
139 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in most adolescents with alopecia areata, but more research is needed.



















