August 2024 in “Journal of Research in Clinical Medicine” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, with some linked to how severe the illness is.
 December 2021 in “The Sri Lanka Journal of Dermatology”
December 2021 in “The Sri Lanka Journal of Dermatology” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, including rashes and lesions.
71 citations,
May 2019 in “Rheumatology” Tph cells are linked to the severity of systemic lupus erythematosus.
40 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” CLASI is a valid tool for assessing skin activity and damage in lupus patients.
A 29-year-old woman with symptoms of both lupus and rheumatoid arthritis improved with specific medications.
78 citations,
January 2013 in “Brachytherapy” HDR electronic brachytherapy effectively treats nonmelanoma skin cancer with good cosmetic results and minimal side effects.
15 citations,
January 2019 in “Breast care” Preventive measures and effective management are crucial for reducing skin side effects in cancer treatment.
 1 citations,
August 2020 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences”
1 citations,
August 2020 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” Skin problems like rashes and hair loss can help diagnose and predict COVID-19.
September 2013 in “International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics” High dose rate electronic brachytherapy is an effective and safe non-surgical treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer with good cosmetic results after three years.
 44 citations,
April 2006 in “Expert opinion on drug safety”
44 citations,
April 2006 in “Expert opinion on drug safety” Gefitinib can cause skin problems, diarrhea, and nausea, but rarely causes severe lung disease or hair loss.
 41 citations,
August 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
41 citations,
August 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus had widespread skin symptoms triggered by medication and sunlight, which improved with specific treatments.
19 citations,
April 2016 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” Nilotinib can cause keratosis pilaris, a skin condition.
 9 citations,
March 1968 in “The BMJ”
9 citations,
March 1968 in “The BMJ” A woman's severe skin reaction was caused by an allergy to a skin treatment.
 2 citations,
December 2023 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology”
2 citations,
December 2023 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology” Late onset SLE has different symptoms and antibody profiles compared to young onset SLE.
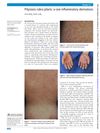 February 2018 in “BMJ case reports”
February 2018 in “BMJ case reports” An 18-year-old woman was diagnosed with a rare skin condition called Pityriasis rubra pilaris.
June 2016 in “Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases” Early symptoms of SLE include fatigue, joint pain, and sensitivity to sunlight.
 January 2006 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2006 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Most studies on perioral dermatitis treatment are of low quality, with some agreement on oral tetracycline effectiveness and stopping steroids and cosmetics.
 44 citations,
April 2011 in “Critical reviews in analytical chemistry”
44 citations,
April 2011 in “Critical reviews in analytical chemistry” Fluconazole is an effective antifungal medication with potential side effects and lacks official analytical methods for its determination.
13 citations,
February 2020 in “CHEST Journal” Vitamin C supplementation can resolve pulmonary arterial hypertension caused by vitamin C deficiency.
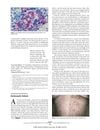 10 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology”
10 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology” A man's chest hair turned white after a shingles infection, possibly due to virus-damaged pigment cells.
1 citations,
November 2020 in “Cermin Dunia Kedokteran” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, helping doctors diagnose it early.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman had a delayed allergic reaction to the blood thinner enoxaparin, treated with a steroid cream.
 1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” ZD1839, a cancer drug, can cause mild skin rashes that are treatable without stopping the medication.
 February 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
February 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Cryptococcoid Sweet syndrome can be linked to hydralazine use and multiple autoantibodies, requiring high clinical suspicion and more research.
 April 2021 in “European medical journal”
April 2021 in “European medical journal” A COVID-19 patient had severe and long-lasting skin issues and unusual hair loss.
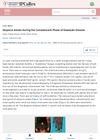 April 2021 in “Indian pediatrics case reports”
April 2021 in “Indian pediatrics case reports” A child's hair loss after Kawasaki disease may help understand the disease's autoimmune causes.
August 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Biotin treatment for hair, nail, and skin disorders has weak evidence and should not be recommended unless new research shows clear benefits.
 March 2017 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
March 2017 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Skin reactions to drugs are most often rashes caused by antibiotics, with nevirapine being the most common culprit; knowing these patterns can improve treatment and outcomes.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus has different forms, is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, and can be treated with various medications, but more targeted therapies are needed.

The document concludes that various skin conditions have specific treatments and that adequate calcium intake may prevent osteoporosis.

















