Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Caused by Skin Hypersensitivity to Monosulfiram
March 1968
in “
The BMJ
”

TLDR A woman's severe skin reaction was caused by an allergy to a skin treatment.
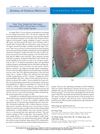
In 1968, a 47-year-old woman with a history of rubber dermatitis developed toxic epidermal necrolysis after using a monosulfiram solution, an antiscabetic agent. She presented with fever, rash, and skin shedding but had normal blood and urine tests, and no bacteria in her pustules. Her condition improved with triamcinolone and fluocinolone treatment, although she experienced temporary hair loss and nail changes, recovering after three months. Patch testing indicated a hypersensitivity to tetramethylthiuram disulphide, related to monosulfiram. This case underscores the risk of severe skin reactions from topical treatments and the need to consider a patient's hypersensitivity history.