
Intermittent fasting slows hair growth by damaging hair follicle cells.
 24 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology”
24 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology” The spiny mouse is a unique menstruating rodent that can help us understand menstruation and reproductive disorders.
 19 citations,
May 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
19 citations,
May 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Minoxidil and finasteride are the best for non-scarring hair loss; more research is needed for scarring hair loss treatments.
119 citations,
June 2021 in “Heliyon” Licorice has many health benefits but should be used carefully due to possible side effects.
March 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Three specific genetic variants cause severe skin issues in children with EBS, highlighting the need for early genetic screening.
 4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology”
4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology” Scalp cooling is the only FDA-approved method to prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, but other treatments like minoxidil and PRP are being tested.
 218 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
218 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Guidelines suggest various treatments for alopecia areata, but leaving it untreated is also an option as 80% cases may recover on their own.
 48 citations,
April 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
48 citations,
April 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” Possible new treatments for common hair loss include drugs, stem cells, and improved transplants.
2 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of pharmacology and pharmacotherapeutics” A woman got unwanted hair growth on her face from using bimatoprost eyedrops for glaucoma.
 6 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of immunology research”
6 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of immunology research” Exosomes from fat-derived stem cells can potentially improve hair growth and could be a new treatment for immune-related hair loss.
 85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition often starting before age 20, with varied treatment success and a need for personalized treatment plans.

L-PGDS has specific binding sites for its functions and could help in drug delivery system design.
 November 2023 in “BMC genomics”
November 2023 in “BMC genomics” The study concluded that the arachidonic acid pathway and the protein KRT79 play a role in determining the fineness of cashmere.
 18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology”
18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology” Lipocalin-Type Prostaglandin D2 Synthase (L-PGDS) is a protein that plays many roles in the body, including sleep regulation, pain management, food intake, and protection against harmful substances. It also affects fat metabolism, glucose intolerance, cell maturation, and is involved in various diseases like diabetes, cancer, and arthritis. It can influence sex organ development and embryonic cell differentiation, and its levels can be used as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions.
April 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Dermal factors are crucial in regulating melanin production in skin.

New treatments for hair loss should target eight main causes and use specific plant compounds and peptides for better results.
 September 2023 in “Medicina-lithuania”
September 2023 in “Medicina-lithuania” The study suggests that analyzing DNA can help treat hair loss, but more research is needed.
 January 2024 in “Journal of Biosciences and Medicines”
January 2024 in “Journal of Biosciences and Medicines” Future treatments for androgenic alopecia may focus on reactivating hair follicle stem cells and improving drug delivery.
70 citations,
September 2017 in “Expert opinion on therapeutic patents” The review suggests that while many AKR1C3 inhibitors show promise for treating certain cancers, more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness in humans.
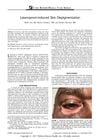 9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma”
9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma” Latanoprost eye drops may cause skin depigmentation.
 8 citations,
January 2016 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery”
8 citations,
January 2016 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery” PRGF treatment is safer and more effective for hair loss than topical minoxidil.
69 citations,
April 2010 in “Clinical ophthalmology” Bimatoprost is effective for growing longer, thicker, and darker eyelashes.
 165 citations,
September 2003 in “Toxicology and applied pharmacology”
165 citations,
September 2003 in “Toxicology and applied pharmacology” Blocking COX, especially COX-2, in the skin can reduce inflammation and pain and may help prevent skin cancer.
 July 2024 in “Applied Sciences”
July 2024 in “Applied Sciences” Bimatoprost is more effective than sweet almond oil for enhancing eyebrow growth.
 April 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Eyelashes are important for looks and eye protection, and more people are treating sparse eyelashes; more research is needed to understand eyelash biology and improve treatments.
 March 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy (Internet)”
March 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy (Internet)” Genetic factors could lead to personalized treatments for hair loss.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Aesthetic & Reconstructive Surgery”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Aesthetic & Reconstructive Surgery” Hair transplantation is the best treatment for hair loss, with new technologies improving results, and stem cell and gene therapies may treat severe baldness in the future.
 August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” New regenerative therapies show promise for treating hair loss.
11 citations,
March 2021 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Treating hair loss in both men and women is effective and improves quality of life.
 26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Regenerative therapies show promise for treating vitiligo and alopecia areata.























