 March 2020 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
March 2020 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Two unusual cases showed that Lichen Planopilaris can look like other skin conditions and need early treatment to protect hair.
 1 citations,
August 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” A patient developed nerve problems as a side effect of a hair loss treatment called tofacitinib.
 July 2024 in “Chinese Medical Journal”
July 2024 in “Chinese Medical Journal” Peripheral blood alive cell treatment is effective and safe for treating hair loss.
48 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Epigenetic changes in blood cells may contribute to alopecia areata.
 20 citations,
June 2010 in “Genes and Immunity”
20 citations,
June 2010 in “Genes and Immunity” Blood tests can help understand the genetic differences in people with alopecia areata, including how severe it is and if it's inherited.
 12 citations,
March 2016 in “BBA clinical”
12 citations,
March 2016 in “BBA clinical” Increased Toll-like receptors in blood cells may contribute to alopecia areata and could be a target for new treatments.
 4 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
4 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Poor response to topical immunotherapy in alopecia areata patients is linked to impaired cell responses.
 1 citations,
October 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
1 citations,
October 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Using healthy donor stem cells can potentially calm overactive immune cells and reduce inflammation in severe hair loss patients, offering a possible treatment method.
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Cell-based therapy using specific immune cells may help treat alopecia areata by promoting hair regrowth.
2 citations,
October 1990 in “PubMed” Severe alopecia areata involves higher levels of certain immune cells, which can be normalized with betamethasone.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study suggests that a specific type of immune cell, memory-like NK cells, may increase during active hair loss in Alopecia areata.
52 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Apremilast may help treat hair loss in alopecia areata.
 23 citations,
January 1994 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
23 citations,
January 1994 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Hair loss in men and women is linked to high stress hormone levels and other hormonal imbalances, suggesting treatments should be customized to each person's hormones.
 14 citations,
September 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
14 citations,
September 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Oral minoxidil improves hair density in women with androgenetic alopecia, with mild side effects.
 10 citations,
October 2018 in “Sexual medicine reviews”
10 citations,
October 2018 in “Sexual medicine reviews” Men using hair loss drugs like finasteride may experience sexual side effects like erectile dysfunction, but it's unclear who will be affected and when. Treating depression and sexual symptoms is suggested, as these men often have higher rates of both. More research is needed to understand why these side effects occur.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Scalp nerve issues are linked to hair loss in men.

Oral Minoxidil could be a safe and effective alternative treatment for various non-androgenic alopecias.
 September 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports”
September 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports” A man got heart and swelling issues from a hair loss medication, so doctors advise careful use, especially in people with past health problems.
 78 citations,
March 2017 in “JAMA Dermatology”
78 citations,
March 2017 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in people with severe alopecia, but side effects occurred and benefits stopped after treatment ended.
75 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Alopecia areata can be triggered by specific immune cells without genetic or environmental factors.
38 citations,
August 1999 in “New England journal of medicine/The New England journal of medicine” Indinavir can cause hair loss and other skin problems.
25 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” A new mouse model helps understand and find treatments for alopecia areata.
 13 citations,
February 2007 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
13 citations,
February 2007 in “British Journal of Dermatology” EF and PXE not closely related.
 12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics”
12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics” Targeting immune tolerance issues in Alopecia Areata could restore hair growth and maintain remission.
 9 citations,
January 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
9 citations,
January 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a poorly understood condition with increasing cases and unclear treatment effectiveness.
 5 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology”
5 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology” Hair loss on the lower legs is common in middle-aged men, usually harmless, and doesn't need treatment.
 3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
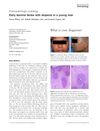
3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A young man was diagnosed with trichoepitheliomas, causing thick skin and hair loss.
2 citations,
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” The conclusion is that a new method could improve the identification of autoimmune targets in alopecia areata, despite some limitations.
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Increased TEMRA cells can predict treatment outcomes in rapidly progressive alopecia areata.
May 2019 in “Journal of clinical oncology” Topical calcitriol was safe and well-tolerated for potential hair loss prevention in chemotherapy patients.



















