 December 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
December 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Alopecia areata needs more recognition and better treatment access in Latin America to improve patient care and outcomes.
 October 2024 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
October 2024 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Higher GPER-1 levels are linked to more severe and shorter-duration androgenetic alopecia, suggesting GPER-1 as a potential treatment target.
[object Object]  August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” New regenerative therapies show promise for treating hair loss.
 January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine”
January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” The document concludes that hair follicle regeneration involves various factors like stem cells, noncoding dsRNA, lymphatic vessels, growth factors, minoxidil, exosomes, and induced pluripotent stem cells.
 14 citations,
March 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
14 citations,
March 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Patients with severe alopecia areata have higher levels of MIF, which decrease after successful treatment.
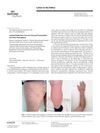 6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” A man with rare Lichen Planopilaris lost body hair, not scalp hair, and treatment stopped itching but didn't regrow hair.
 20 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
20 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Eye exams are crucial for kids with 13q deletion syndrome, tamoxifen can cause vision loss, Propecia may lead to cataracts, Lipoid Proteinosis causes skin bumps, and OCT is useful for diagnosing macular diseases.
 13 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
13 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” A baby boy with 13q deletion syndrome had eye cancer, a woman's vision improved after stopping a breast cancer drug, a man developed cataracts from using Propecia, and a rare skin disorder called Lipoid Proteinosis was discussed. Also, a tool called OCT is useful for diagnosing macular diseases.
 9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” The document discusses various eye conditions and their treatments, including a rare eye cancer in a baby, vision loss from a cancer drug, cataracts from a baldness treatment, a rare skin disorder, and a specific type of eye disease diagnosed with a special imaging technique.
 5 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
5 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Multiple eye conditions were studied, highlighting the importance of various imaging methods for diagnosis, the vision side effects of drugs tamoxifen and Propecia, and the usefulness of optical coherence tomography for diagnosing and monitoring macular and retinal diseases.
134 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental dermatology” Hair follicles are normally protected from the immune system, but when this protection fails, it can cause hair loss in alopecia areata.
[object Object]  January 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
January 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Hydroxychloroquine is less effective than betamethasone oral mini pulse therapy for treating alopecia areata.
 165 citations,
June 2007 in “European Journal of Cell Biology”
165 citations,
June 2007 in “European Journal of Cell Biology” Hair follicle stem cells are key for hair and skin regeneration, can be reprogrammed, and have potential therapeutic uses, but also carry a risk of cancer.
 63 citations,
January 1984 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
63 citations,
January 1984 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil promotes hair growth by increasing cell division and DNA synthesis.
 54 citations,
January 1983 in “Archives of Dermatology”
54 citations,
January 1983 in “Archives of Dermatology” KFSD is a rare condition causing scarring hair loss, with no effective treatment known at the time of the report.
 42 citations,
March 2008 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
42 citations,
March 2008 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Hormones and neuroendocrine factors control hair growth and color, and more research could lead to new hair treatment options.
 42 citations,
March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies”
42 citations,
March 2006 in “Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies” The conclusion is that we need more effective hair loss treatments than the current ones, and these could include new drugs, gene and stem cell therapy, hormones, and scalp cooling, but they all need thorough safety testing.
 23 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
23 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” A boy with chromosome 13q deletion syndrome developed eye cancer, a woman with breast cancer lost vision due to a rare side-effect of her treatment, a man's vision worsened after using a hair loss drug, and two rare disorders were discussed. Optical Coherence Tomography is useful for diagnosing and monitoring these conditions.
 11 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
11 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hyaluronic acid injections can cause hair loss due to blocked blood vessels.
 11 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
11 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Taking Propecia might lead to the development of cataracts.
 7 citations,
April 2021 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
7 citations,
April 2021 in “Dermatology and Therapy” H-1 antihistamines may help with various skin conditions, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 7 citations,
April 2018 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
7 citations,
April 2018 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” BeauTop helps hair grow by increasing certain growth factors.
 7 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
7 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Finasteride, often used for hair loss, can potentially cause cataracts.
 6 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
6 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” The document concludes that careful diagnosis is crucial for chromosome 13q deletion syndrome, tamoxifen can cause reversible eye damage, finasteride may be linked to cataracts, and OCT is useful for diagnosing macular diseases.
 4 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
4 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” New treatments targeting T-cell pathways are needed for better alopecia areata management.
 3 citations,
February 2016 in “Pediatric dermatology”
3 citations,
February 2016 in “Pediatric dermatology” Strong skin creams work well for long-term scalp inflammation in Rapp-Hodgkin Ectodermal Dysplasia.
 April 1906 in “The American Journal of the Medical Sciences”
April 1906 in “The American Journal of the Medical Sciences” Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans causes skin scarring and might be treated with a new synthetic retinoid.
40 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic clinics” More research is needed to understand the genetic causes of Alopecia areata to develop better treatments.
91 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” NK cells play a role in skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis.
13 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis” Higher MIF levels in alopecia areata patients suggest it could be a treatment target and disease predictor.


























