 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Some hair loss disorders cause permanent loss due to scarring, and treatments like steroids don't always work well.
 June 2008 in “Springer eBooks”
June 2008 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that permanent hair loss conditions are complex, require early specific treatments, and "secondary permanent alopecias" might be a more accurate term than "secondary cicatricial alopecia."
 182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some treatments can help with a hair loss condition called alopecia areata, but none ensure lasting results; choices depend on the person, with JAK inhibitors showing promise for severe cases.
 56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
 49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Effective management of children's hair loss involves accurate diagnosis, various treatments, and supportive care.
 20 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
20 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The conclusion is that understanding and addressing the psychological effects of alopecia areata is important for effective treatment.
 17 citations,
June 2016 in “Croatian Medical Journal”
17 citations,
June 2016 in “Croatian Medical Journal” Patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease often have skin problems like vitiligo and alopecia areata.
5 citations,
January 2020 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” Injecting platelet-rich plasma or applying it with a laser or microneedling can treat hair loss effectively. The laser and microneedling methods cause less pain.
 4 citations,
July 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
4 citations,
July 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” New biopsy techniques and tools improve alopecia diagnosis, and both too much and too little selenium can cause hair loss.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
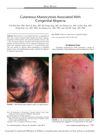 3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.

Herbal remedies might help with hair loss but need more research for safety and effectiveness.
 October 2023 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences”
October 2023 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences” Personalized treatment plans combining natural and synthetic approaches are important for managing alopecia effectively.
 January 2020 in “Der Pharmacia Lettre”
January 2020 in “Der Pharmacia Lettre” Nanoparticle-based herbal remedies could be promising for treating hair loss with fewer side effects and lower cost, but more research is needed.
 November 2017 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research”
November 2017 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research” Three compounds from Dadap leaves may help treat hair loss.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Hair pulling disorder is treated with therapy and medication; hair loss from tension can be reversed if caught early.
 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.

Hair loss in African American women, caused by hair care, genetics, and environment, needs more research for better treatment.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition often starting before age 20, with varied treatment success and a need for personalized treatment plans.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
 28 citations,
December 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
28 citations,
December 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Monochromatic light devices, especially the 308-nm excimer laser, are promising for treating alopecia areata but more research is needed.
 26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Regenerative therapies show promise for treating vitiligo and alopecia areata.
 24 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
24 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Use specific tools to measure quality of life in alopecia areata patients and improve future treatments.
 23 citations,
October 2018 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Safety”
23 citations,
October 2018 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Safety” Consider benefits and risks of new alopecia treatments for safety.
 6 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
6 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Combining mometasone furoate cream with adapalene gel is safer and more effective for hair regrowth in alopecia areata than using the cream alone.
 6 citations,
November 2007 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice”
6 citations,
November 2007 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of alopecia in children relies on thorough examination and history, and while treatments exist, none can alter the course of alopecia areata, which can significantly affect a child's psychological well-being.
 3 citations,
November 2020 in “Curēus”
3 citations,
November 2020 in “Curēus” A child's hair loss from alopecia areata was fully reversed in five months using diet and supplements.
 2 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in microbiology”
2 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in microbiology” The health of the gut may be important in developing new ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat alopecia areata.
 August 2024 in “OSMANGAZİ JOURNAL OF MEDICINE”
August 2024 in “OSMANGAZİ JOURNAL OF MEDICINE” The visfatin GT genotype may increase the risk of Alopecia Areata.





























