 April 2024 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
April 2024 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Tofacitinib is effective for severe alopecia areata, similar to oral betamethasone.
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” Oral mini-pulse methylprednisolone is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.

Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, may be passed through T cells and has genetic links, while treatments vary in effectiveness. Male pattern baldness can be treated with finasteride and is influenced by androgens in hair follicles.
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology” Methylprednisolone infusions can help some people with severe alopecia regrow hair.
4 citations,
January 2014 in “JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH” Oral minipulse therapy effectively treated bullous lichen planus in a 35-year-old woman.
 21 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” The combination of cyclosporine and PUVA might help treat severe alopecia areata.
 17 citations,
August 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
17 citations,
August 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that oral finasteride and topical minoxidil are effective for genetic hair loss, while other treatments for different types of hair loss show promise but need more research.
 8 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
8 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Both individual and combined treatments of tofacitinib and corticosteroids can help regrow hair in moderate-to-severe alopecia areata, but ongoing treatment may be necessary.
 164 citations,
April 2008 in “Cochrane library”
164 citations,
April 2008 in “Cochrane library” Current treatments for alopecia show no significant long-term benefits.
 January 2019 in “ARC journal of pharmaceutical sciences”
January 2019 in “ARC journal of pharmaceutical sciences” Acne can be managed with various treatments and requires psychological support due to its emotional impact.
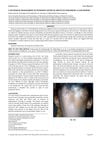 March 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
March 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Combining OMP with cyclosporine can effectively treat severe alopecia areata in children.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta Medica Philippina”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta Medica Philippina” Azathioprine may help treat severe alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 18 citations,
June 2019 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
18 citations,
June 2019 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Acne can't be cured but can be managed with treatments like benzoyl peroxide and diet changes; it's costly and can lead to scarring and mental health issues.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Combination therapies might work better for some vitiligo patients, but results vary.
1 citations,
January 2013 in “International journal of trichology” The treatment using phenol and dexamethasone was effective for alopecia areata with no recurrence in 6 months.
 4 citations,
January 2022 in “Drug design, development and therapy”
4 citations,
January 2022 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Intramuscular corticosteroids are effective and safe for severe alopecia areata, with most patients regrowing hair, but nearly half may relapse.
 18 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinical Drug Investigation”
18 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinical Drug Investigation” Low-dose isotretinoin combined with pulsed azithromycin cleared acne in most patients, with mild side effects.
 February 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery”
February 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery” The combined treatment helps improve severe hair loss and reduces the need for other medications.
 40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Systemic glucocorticosteroids are a primary treatment for various skin conditions but require careful management due to potential side effects and relapses.
 13 citations,
August 2020 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings”
13 citations,
August 2020 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings” Women with lichen planopilaris often have thyroid disease, depression, anxiety, and may respond to treatment with slowed disease progression.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.
 76 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
76 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and FDA-approved treatments for different types of hair loss exist, but treatments for severe cases often fail and future improvements may focus on hair follicle stem cells.
 20 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
20 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The document says that treating the root cause of hair follicle damage is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss, and treatment options vary.
1 citations,
August 2005 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease with genetic links, treatable with certain medications, and can affect mental health.
78 citations,
August 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” New vitiligo treatments focus on controlling immune damage and restoring skin color.
 4 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
4 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Case reports are important in medical science for discovering drugs and identifying rare conditions, despite their limitations.
 29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery”
29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition treated with corticosteroids, and histologic confirmation is the best diagnosis method.
 17 citations,
March 2018 in “Pediatric dermatology”
17 citations,
March 2018 in “Pediatric dermatology” Hydroxychloroquine may help treat alopecia areata in children.

New treatments for vitiligo may focus on protecting melanocyte stem cells from stress and targeting specific pathways involved in the condition.























