 1 citations,
January 1967 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
January 1967 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that while some hair and scalp disorders can be treated, hair loss from destroyed follicles is permanent, and damaged hair can only regrow naturally.
 69 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
69 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Trichoscopy is a quick, noninvasive method to diagnose hair and scalp disorders, often reducing the need for biopsies.
 14 citations,
March 2022 in “Journal of inflammation research”
14 citations,
March 2022 in “Journal of inflammation research” Baricitinib shows promise as a new treatment for certain skin conditions like alopecia areata.
 34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Some treatments work for common baldness, but there's less evidence for other hair loss types, and more research is needed.
 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Trichoscopy and trichogram are useful for diagnosing hair and scalp conditions.
 41 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
41 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Psoriasis can cause temporary or permanent hair loss.
 22 citations,
January 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
22 citations,
January 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The meeting focused on understanding, diagnosing, and finding treatments for irreversible hair loss diseases.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
 April 2024 in “Lasers in medical science”
April 2024 in “Lasers in medical science” Lasers and light therapies are effective in promoting hair regrowth for different types of hair loss.
 February 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
February 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” A boy's hair, nails, and skin improved after 6 months of steroid treatment.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Cryotherapy may be an effective and simple treatment for mild hair loss with few side effects.
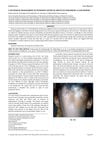 March 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
March 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Combining OMP with cyclosporine can effectively treat severe alopecia areata in children.
 11 citations,
November 2019 in “Clinical Case Reports”
11 citations,
November 2019 in “Clinical Case Reports” A Brazilian teenager with severe hair loss had total hair regrowth with no side effects after using tofacitinib.
 18 citations,
May 2016 in “Annals of Medicine”
18 citations,
May 2016 in “Annals of Medicine” The article concludes that correctly diagnosing systemic causes of hair loss requires a detailed clinical evaluation and a systematic diagnostic approach.
 July 2021 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences”
July 2021 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences” Homeopathic treatment can help manage alopecia areata in children.
9 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology” Combining calcipotriol with mometasone is more effective for treating alopecia areata than using mometasone alone.
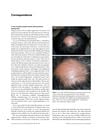 11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Greying hairs may be protected from alopecia areata.
 13 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
13 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that a new system using the SALT score should replace the current alopecia areata classification for better accuracy in assessing severity and prognosis.
 February 2019 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
February 2019 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Psychological stress is a major factor in the onset and severity of alopecia areata, with atopic individuals being more prone to develop it.
19 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of Dermatology” Early high-dose steroid treatment helps prolong disease-free periods in severe alopecia areata.
 December 2023 in “International journal of multidisciplinary research and analysis”
December 2023 in “International journal of multidisciplinary research and analysis” SH-MSCs gel reduced IL-6 and increased TGF-β, suggesting it could treat alopecia.
 4 citations,
October 2016
4 citations,
October 2016 Herbs like aloe vera and amla are effective and safe for treating hair loss.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.
 October 2024 in “Journal of Education Health and Sport”
October 2024 in “Journal of Education Health and Sport” Alopecia areata treatment should be personalized, using topical or systemic therapies based on severity, with promising options like JAK inhibitors needing more research.
 6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib may effectively treat Alopecia Areata.
 13 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
13 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Cyclosporine combined with corticosteroids is more effective for severe alopecia areata than cyclosporine alone.
 182 citations,
October 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
182 citations,
October 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The 2003 guidelines suggest that while some treatments can regrow hair in alopecia areata, none alter the disease's progression, and wigs may be the best option for extensive hair loss.
 40 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
40 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” JAK inhibitors show promise for treating skin and hair disorders but need more research on long-term safety and effectiveness.
 13 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
13 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Patchy alopecia areata can affect only pigmented hairs, leaving gray hairs untouched.




























