 7 citations,
May 2022 in “PLOS ONE”
7 citations,
May 2022 in “PLOS ONE” Certain genes and pathways are linked to the production of finer and denser wool in Hetian sheep.
[object Object]  438 citations,
October 2010 in “Oncogene”
438 citations,
October 2010 in “Oncogene” Keratins help protect cells, aid in cancer diagnosis, and influence cancer behavior and treatment.
28 citations,
December 2005 in “Oncogene”  3 citations,
May 2022 in “Oncogene”
3 citations,
May 2022 in “Oncogene” Vav2 and Vav3 proteins help control skin stem cell numbers and activity in both healthy and cancerous cells.
 68 citations,
September 2018 in “Trends in Cell Biology”
68 citations,
September 2018 in “Trends in Cell Biology” Cancer can hijack the body's cell repair system to promote tumor growth, and targeting this process may improve cancer treatments.
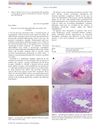 5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Sorafenib can cause delayed skin problems, so patients need careful monitoring.
 232 citations,
January 2013 in “Nature Cell Biology”
232 citations,
January 2013 in “Nature Cell Biology” Understanding where cancer cells come from helps create better prevention and treatment methods.
 38 citations,
February 2012 in “Supportive Care in Cancer”
38 citations,
February 2012 in “Supportive Care in Cancer” Skin problems like acne, dry skin, and nail and hair changes are common in patients taking EGFR inhibitors.
 33 citations,
January 2018 in “The International Journal of Developmental Biology”
33 citations,
January 2018 in “The International Journal of Developmental Biology” Cell aging can be both good and bad for tissue repair.
 5 citations,
September 2010 in “Cancer Prevention Research”
5 citations,
September 2010 in “Cancer Prevention Research” The research suggests new treatments for skin cancer could target specific cell growth pathways.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Targeted therapies for lung cancer are effective but require careful management of side effects to benefit patients.
 July 1996 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
July 1996 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism” The book is a valuable reference on androgenic disorders for professionals but not suitable for laypeople or medical students.
 351 citations,
February 2010 in “Nature Cell Biology”
351 citations,
February 2010 in “Nature Cell Biology” Basal cell carcinoma mostly starts from cells in the upper skin layers, not hair follicle stem cells.
 308 citations,
September 2010 in “Nucleic acids research”
308 citations,
September 2010 in “Nucleic acids research” Increasing mir-302 turns human hair cells into stem cells by changing gene regulation and demethylation.
 144 citations,
August 2019 in “Cells”
144 citations,
August 2019 in “Cells” The WNT signaling pathway is important in many diseases and targeting it could offer new treatments.
 133 citations,
May 2016 in “Cell Host & Microbe”
133 citations,
May 2016 in “Cell Host & Microbe” Human dermal fibroblasts are the main cells targeted by a virus that can cause a deadly skin cancer, and a certain inhibitor can effectively block this infection.
 68 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology”
68 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology” The document concludes that targeting the androgen receptor may be a promising breast cancer treatment, especially for certain types.
 66 citations,
March 2019 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences”
66 citations,
March 2019 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences” Melanocyte development from neural crest cells is complex and influenced by many factors, and better understanding could help treat skin disorders.
 66 citations,
December 2013 in “Nature Cell Biology”
66 citations,
December 2013 in “Nature Cell Biology” Inactive hair follicle stem cells help prevent skin cancer.
[object Object]  64 citations,
July 2016 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
64 citations,
July 2016 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The p53 protein has complex, sometimes contradictory functions, including tumor suppression and promoting cell survival.
 44 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell Death & Differentiation”
44 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell Death & Differentiation” Tumor suppressors help control inflammation in cancer and restoring their function could lead to new treatments.
 43 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
43 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Organotypic culture systems can grow skin tissues that mimic real skin functions and are useful for skin disease and hair growth research, but they don't fully replicate skin complexity.
 36 citations,
August 2011 in “Experimental Dermatology”
36 citations,
August 2011 in “Experimental Dermatology” Eccrine sweat gland's clear cells likely cause excessive sweating in hyperhidrosis.
 32 citations,
February 2017 in “Oncotarget”
32 citations,
February 2017 in “Oncotarget” Cellular senescence has both cancer-blocking and cancer-promoting effects, and targeting senescent cells may improve health and lifespan.
 30 citations,
April 2010 in “Cell Cycle”
30 citations,
April 2010 in “Cell Cycle” The gene p53 is crucial for removing damaged cells to allow for healthy tissue renewal.
 27 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
27 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The conclusion is that androgenetic alopecia and senescent alopecia have unique gene changes, suggesting different causes and potential treatments for these hair loss types.
 26 citations,
May 2012 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences”
26 citations,
May 2012 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences” NcoA4 may have roles beyond helping control gene activity, possibly affecting cell behavior and stability.
 25 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of mammary gland biology and neoplasia”
25 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of mammary gland biology and neoplasia” Hedgehog signaling is crucial for mammary gland development over hair follicles.
 21 citations,
March 2019 in “Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences”
21 citations,
March 2019 in “Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences” The androgen receptor is a promising target for breast cancer treatment, especially in triple-negative cases, but more research is needed for personalized therapies.
 21 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
21 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology” New treatments for advanced skin cancer are improving patient outcomes, but drug resistance and finding the right treatment combinations are still big challenges.





























