 15 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology” Some patients with a type of skin lymphoma can experience a rare, non-scarring hair loss that looks like another hair loss condition but has distinct features.
 January 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
January 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” Trichoscopy shows black dots, yellow dots, and empty follicles are common in Alopecia Areata, with broken and exclamation mark hair as typical patterns.
 October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The most effective treatments for hair loss are minoxidil, finasteride, PRP, and hair transplants, with steroids and immunosuppressants for autoimmune types.
 45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” Topical immunotherapy, especially with DPCP, is effective for treating severe alopecia areata.
 March 2022 in “Wound practice & research”
March 2022 in “Wound practice & research” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but standardized guidelines are needed.
 32 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
32 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Low vitamin D might be linked to certain types of hair loss, and supplements could help, but more research is needed.
 27 citations,
September 2017 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
27 citations,
September 2017 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Topical tofacitinib may grow hair better than minoxidil by increasing VEGF and reducing inflammation.
 18 citations,
November 2018 in “Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore”
18 citations,
November 2018 in “Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore” Sulfasalazine can cause severe allergic reactions leading to long-term autoimmune issues like hair loss and skin discoloration.
 3 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Nepal Medical Association”
3 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Nepal Medical Association” A woman with complete hair loss and severe hyperthyroidism was successfully treated with azathioprine and hydroxychloroquine.
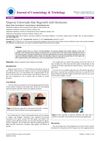 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 6 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Chemotherapy”
6 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Chemotherapy” A man lost all his hair as a rare side effect after hepatitis C treatment.
 14 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
14 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Advanced therapies like gene, cell, and tissue engineering show promise for hair regrowth in alopecia, but their safety and effectiveness need more verification.
 December 2022 in “Cureus”
December 2022 in “Cureus” Low iron levels are linked to hair loss in women.
 19 citations,
September 2011 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
September 2011 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Transverse scalp sections are better for diagnosing non-scarring hair loss, while vertical sections are better for a specific scarring hair loss called lichen planopilaris.
 1 citations,
April 2022 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
1 citations,
April 2022 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Fractional laser therapy may help regrow hair in alopecia areata.
 170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology”
170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology” The conclusion is that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires good teamwork between skin doctors and lab experts.
 19 citations,
January 2018
19 citations,
January 2018 Most people with alopecia areata have nail changes, which are common but don't greatly affect their quality of life.
 16 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy”
16 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy” New treatments for hair loss are showing promise due to better understanding of genetics and the immune system.
 16 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of Medical Primatology”
16 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of Medical Primatology” The monkey's hair loss was due to an autoimmune disease, not genetics.
 8 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
8 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Hepatitis C treatment may trigger complete hair loss, especially in those with a history of patchy hair loss, but hair usually grows back within a year.
 3 citations,
May 2010 in “Nursing Standard”
3 citations,
May 2010 in “Nursing Standard” Treatments for autoimmune hair loss have limited success and often relapse, and emotional support is crucial for those affected.
 1 citations,
May 2010 in “Nursing Standard”
1 citations,
May 2010 in “Nursing Standard” Treatments for autoimmune hair loss have limited success and patients need emotional support and self-acceptance.
 December 2023 in “EPRA international journal of multidisciplinary research”
December 2023 in “EPRA international journal of multidisciplinary research” Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss, has genetic links, and can be managed but not cured.
 June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” The Middle East and Africa need better data, treatment consensus, and support for Alopecia Areata.
 23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology”
23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology” Alopecia areata involves immune response and gene changes affecting hair loss.
 2 citations,
February 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
February 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, environment, and possibly improved by anti-MIF therapy, with many patients experiencing regrowth within a year.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Prospects in Pharmaceutical Sciences”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Prospects in Pharmaceutical Sciences” New cytokine-targeted therapies show promise for treating alopecia areata.
 44 citations,
November 1998 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
44 citations,
November 1998 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Accurate diagnosis is key for treating different kinds of hair loss, and immune response variations may affect the condition and treatment results.
 April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, linked to genetic factors and immune system issues, with no cure yet.
 9 citations,
June 2019 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
9 citations,
June 2019 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Both topical calcipotriol and narrowband UVB improved alopecia, but combining them didn't enhance the effect on hair loss severity, despite higher vitamin D3 levels.






























