 January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Bald men with male pattern baldness still have hair stem cells, but lack certain cells needed for hair growth.
 January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
January 2011 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Bald men with male pattern baldness still have hair stem cells, but lack certain cells needed to grow hair.
 September 2024 in “Ain Shams Medical Journal”
September 2024 in “Ain Shams Medical Journal” Androgenic alopecia causes hair thinning, and treatments include minoxidil, finasteride, and light therapy.
 62 citations,
April 2004 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
62 citations,
April 2004 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Finasteride effectively treats male pattern baldness, improving hair growth and density.
 30 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The conclusion is that future hair loss treatments should target the root causes of hair thinning, not just promote hair growth.
 June 2023 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
June 2023 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” New treatments for male pattern hair loss look promising, but established treatments are still the main option.
 January 2014 in “American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences”
January 2014 in “American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences” Minoxidil, originally a blood pressure medication, is effective in treating hair loss in men and women, with different strengths recommended for each.
 112 citations,
October 2005 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings”
112 citations,
October 2005 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” Minoxidil and finasteride can slow hair loss and stimulate regrowth, but won't restore all lost hair or reverse complete baldness.
 49 citations,
December 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
49 citations,
December 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Dupilumab may cause significant hair loss, which can reverse after stopping the drug.
 16 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
16 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Scalp biopsies from dermatomyositis patients show chronic hair loss without scarring, with mucin and blood vessel changes being very common.
 7 citations,
January 1981 in “Springer eBooks”
7 citations,
January 1981 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that hair biology is complex and there are still unanswered questions about hair loss and follicle changes.
 4 citations,
June 2017 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
4 citations,
June 2017 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” Aryl hydrocarbon receptor overexpression found in miniaturized hair follicles in female hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Transverse scalp biopsy sections help diagnose different alopecias by showing hair follicle details and inflammation patterns.
 1 citations,
July 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Normal hair thickness varies by scalp area and a mix of hair thicknesses is typical in healthy individuals.
 July 2024 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology”
July 2024 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Pilose antler extracts help hair growth by activating hair follicle stem cells.
 April 2024 in “Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal”
April 2024 in “Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal” Androgenetic alopecia is a common hair loss condition influenced by various factors and linked to psychosocial and cardiovascular issues.
 February 2024 in “Biomedicines”
February 2024 in “Biomedicines” Hormones like androgens, estrogen, thyroid hormones, and stress hormones can contribute to hair loss, and treatments target these hormonal imbalances.
September 2023 in “Membranes” 3D-printed membranes with smart sensors can greatly improve tissue healing and have many medical applications.
 July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Androgens like testosterone affect skin health and can lead to conditions such as acne and hair loss, with various treatments available.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Telogen effluvium is a common hair loss condition where many hairs enter the resting phase, often not noticeable until significant loss occurs, and treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
January 2005 in “Farmaceutski glasnik” Minoxidil and finasteride are key treatments for hair loss.
June 2020 in “Journal of Drugs in Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia can be misdiagnosed as androgenetic alopecia in African American women.
 June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal”
June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal” Multi-omics techniques help understand the molecular causes of androgenetic alopecia.
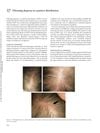 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution is a unique hair loss condition with inflammation and scarring, resembling but distinct from common balding.
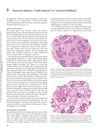 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Senescent alopecia is a type of hair loss that occurs after age 50, not caused by genetics, and involves a gradual thinning of hair without significant inflammation.
 1 citations,
July 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology”
1 citations,
July 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology” Patients with androgenetic alopecia have thinner subcutaneous fat layers in their frontal scalp compared to healthy individuals.
 May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia in men is genetic and linked to health issues like obesity and heart disease, with treatments including minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants.
 30 citations,
December 2017 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
30 citations,
December 2017 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Parietal scalp area has lower hair density and smaller hair diameter in women with hair loss.
 1 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatological reviews”
1 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatological reviews” AGA, a common hair loss, is caused by genetics, hormones, age, and environmental factors.
 July 2004 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
July 2004 in “Dermatologic Surgery” A woman had temporary hair loss due to a stress-related condition after a facelift.


























