 19 citations,
March 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
19 citations,
March 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The tattoo machine method safely delivers an average of 1,175 µg/cm² of medication into the skin.
 12 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
12 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Minoxidil, applied on the skin or taken orally, can improve hair growth in kids, but more research is needed due to possible side effects.
 10 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
10 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Most patients with telogen effluvium had low iron and vitamin D levels; iron supplements were commonly prescribed.
 5 citations,
March 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Biotin supplementation during isotretinoin treatment for acne may help maintain skin hydration and improve hair growth.
 4 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Thread monofilament and minoxidil together increase hair growth in female androgenetic alopecia.
 1 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology”
1 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology” The new hyaluronic acid gel is as safe and effective for lip enhancement as the existing product.
 1 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatological reviews”
1 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatological reviews” AGA, a common hair loss, is caused by genetics, hormones, age, and environmental factors.
 1 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Men with thinner hair from genetic hair loss may be more likely to have an enlarged prostate.
 March 2024 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology”
March 2024 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology” HASHA is a safe and effective option for chin augmentation.
 June 2002 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
June 2002 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Using a microscope during hair transplants cuts damage to follicles in half and could improve hair growth.
 May 2021 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
May 2021 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Minoxidil and photobiomodulation together improve hair growth better than minoxidil alone.
 4 citations,
February 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps diagnose hairline recession causes in Egyptian women, with androgenetic alopecia being the most common.
 2 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Differences in gene expression and methylation patterns found in AGA patients suggest potential targets for future treatments.
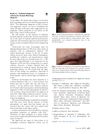 8 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The authors updated the criteria for diagnosing frontal fibrosing alopecia, making it easier to diagnose without a biopsy.
 3 citations,
August 2017 in “Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases”
3 citations,
August 2017 in “Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases” Using platelet-rich plasma and fat grafting to treat nerve pain showed promising results with no side effects.
 32 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)”
32 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)” COVID-19 infection may trigger alopecia areata in some patients.
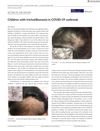 5 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
5 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” More children are showing signs of hair-pulling disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic due to stress and lack of social interaction.
365 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” People with atopic dermatitis have different skin bacteria, and targeting these bacteria might help treat the condition.
 39 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD International”
39 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD International” COVID-19 patients often experience hair loss and scalp pain, which may be related to the severity of their infection and treatment drugs.
 7 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair loss (telogen effluvium) cases rose during the pandemic, especially in Hispanic and non-White groups, and were linked to other health issues and COVID-19.
3 citations,
September 2018 in “JAAD case reports” A Japanese man with rare skin conditions improved with hydroxychloroquine treatment.
2 citations,
September 2018 in “JAAD case reports” A rare type of skin cancer with mucosal involvement was partially treated but eventually relapsed.
 12 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The COVID-19 pandemic increased symptoms in people with skin picking and hair pulling disorders.




















