 2 citations,
March 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
2 citations,
March 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” A 15-year-old boy's severe scalp condition improved significantly with adalimumab and baricitinib treatment.
 June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” ILC1-like cells can cause alopecia areata by attacking hair follicles.
ILC1-like cells can independently cause alopecia areata by affecting hair follicles.
[object Object] 29 citations,
December 2019 in “Expert review of clinical pharmacology” JAK inhibitors are a promising new treatment for hair loss and nail problems in alopecia areata.
14 citations,
July 2022 in “Nutrients” Vitamin A is important for healthy skin and hair, influencing hair growth and skin healing, but UV light reduces its levels.
 8 citations,
July 2022 in “Biomedicines”
8 citations,
July 2022 in “Biomedicines” Autophagy helps keep skin healthy and may improve treatments for skin diseases.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Methods”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Methods” The document explains how to create detailed biological pathways using genomic data and tools, with examples of hair and breast development.
1 citations,
April 2022 in “Applied sciences” Bitter melon extract may help prevent hair loss and can be used in cosmetic products.
 7 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology & research”
7 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology & research” The compound 16 from the Merremia peltata plant could potentially be a good treatment for hair loss (alopecia) due to its strong activity and favorable skin absorption.
 September 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Reducing the dose of Baricitinib to 2mg led to a loss of hair regrowth benefits in nearly half of the patients by Week-104.
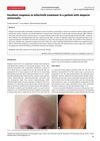 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
 30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” New treatments targeting immune pathways show promise for severe hair loss but need more research for safety and effectiveness.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “JAMA Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “JAMA Dermatology” Increasing the dose of baricitinib to 4 mg helps more patients with severe alopecia areata regrow hair.
 63 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
63 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help treat some skin conditions but need more research.
5 citations,
September 2020 in “Proceedings - Baylor University. Medical Center” Tofacitinib successfully treated a woman's severe symptoms from a rare autoimmune condition.
 3 citations,
March 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Tildrakizumab showed limited effectiveness in treating chronic alopecia areata in a small group of patients.
 16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ruxolitinib may help treat hair loss by reducing inflammation, promoting hair growth signals, and protecting hair follicle immunity.
 51 citations,
July 2010 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
51 citations,
July 2010 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Prolactin may play a significant role in skin and hair health and could be a target for treating skin and hair disorders.
 July 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
July 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Assessing CD8+ T cell levels before surgery may improve vitiligo treatment outcomes.
 October 2022 in “Journal of experimental and clinical medicine”
October 2022 in “Journal of experimental and clinical medicine” Repurposing existing drugs for COVID-19 shows promise but requires more research to confirm effectiveness.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy”
January 2025 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy” Baricitinib is effective for treating severe alopecia areata in Japanese patients, but long-term safety needs more study.
 52 citations,
January 2022 in “Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery”
52 citations,
January 2022 in “Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery” New treatments for COVID-19 show promise, but more effective antiviral drugs are needed.
15 citations,
February 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” Leptin, a hormone from fat cells, affects immune responses and can influence skin diseases and hair growth.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology” The article concludes that treating hair loss requires careful research, understanding the causes, and personalized treatment plans.
 83 citations,
June 2018 in “Frontiers in immunology”
83 citations,
June 2018 in “Frontiers in immunology” Certain types of T cells are essential for healthy skin and play a role in skin diseases, but more research is needed to improve treatments.
 6 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in drug discovery”
6 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in drug discovery” Some small molecule antivirals show promise against COVID-19, but more research is needed to understand and improve them.
[object Object] March 2017 in “Current dermatology reports” Topical JAK inhibitors can effectively treat alopecia areata and vitiligo by modulating immune responses.
 1 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Using minoxidil and tofacitinib together can effectively treat severe hair loss.
 January 2024 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal”
January 2024 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal” Early genetic testing and JAK inhibitors can help treat systemic inflammation in SAVI patients.
 4 citations,
April 2020 in “JAAD case reports”
4 citations,
April 2020 in “JAAD case reports” JAK inhibitors help hair regrowth but not fully effective for androgenetic alopecia.






















