 March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Trichoscopy helps detect early complications in hair transplants and ensures quality in the procedure.
 29 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
29 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Testosterone may influence COVID-19 severity and outcomes.
 April 2024 in “International Research Journal Of Modernization In Engineering Technology And Science”
April 2024 in “International Research Journal Of Modernization In Engineering Technology And Science” Herbal shampoos are effective, non-toxic alternatives for treating dandruff and hair fall.
February 2021 in “International journal of regenerative medicine” A new method using fat tissue cells may help treat hair loss.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Lichen planopilaris is a rare, chronic condition causing hair loss, mainly in middle-aged women, and early treatment is important to prevent permanent baldness.
1 citations,
August 2016 in “Hanbang an'i'bi'in'hu pibu'gwa haghoeji” YangHyulEum Gami-Bang extract may help treat hair loss.
13 citations,
July 2020 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Trichoscopy can help diagnose and monitor the progression of dissecting cellulitis.
 May 2023 in “Brazilian Journal of Animal and Environmental Research”
May 2023 in “Brazilian Journal of Animal and Environmental Research” Photobiomodulation effectively treats hair loss in dogs with black hair follicular dysplasia.
 26 citations,
November 2016 in “European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology”
26 citations,
November 2016 in “European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology” Valproic acid helps delay hair loss and increases survival time for high-grade glioma patients undergoing radiation therapy.
 July 2022 in “International journal of pharmacognosy and life science”
July 2022 in “International journal of pharmacognosy and life science” Mangrove plants have many health benefits and help prevent soil erosion and baldness.

Coconut oil and turmeric were almost as good as 2% ketoconazole shampoo for treating dandruff.
 October 2023 in “International journal of research in Ayurveda and pharmacy”
October 2023 in “International journal of research in Ayurveda and pharmacy” Keedari thailam is effective for treating alopecia areata and has multiple health benefits.
 12 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
12 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” COVID-19 patients may experience temporary hair loss, mainly in women, which is likely reversible.
 8 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine”
8 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine” Dental pulp stem cells are better for tissue repair, while fat tissue stem cells may be more suited for wound healing and hair growth.
 5 citations,
June 2021 in “JAAD Case Reports”
5 citations,
June 2021 in “JAAD Case Reports” Platelet-rich plasma therapy may help treat folliculitis decalvans but benefits might not last without ongoing treatment.
 35 citations,
January 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics”
35 citations,
January 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Tinea capitis is a common scalp infection causing hair loss, mostly in young children.
3 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of cosmetics, dermatological sciences and applications” Many Iraqi patients had skin problems at the site where a vein was taken for heart surgery.
 27 citations,
January 2002 in “Exogenous Dermatology”
27 citations,
January 2002 in “Exogenous Dermatology” Chronic exposure to sunlight may worsen male pattern baldness and protecting the scalp from the sun could slow it down.
 February 2023 in “Aesthetic Cosmetology and Medicine”
February 2023 in “Aesthetic Cosmetology and Medicine” Medicinal plants in nutricosmetics contain compounds that can improve skin and hair health.
January 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences” During the COVID-19 lockdown, there were fewer cases of mild skin issues and more cases of stress-related skin conditions.
 May 2020 in “International journal of current microbiology and applied sciences”
May 2020 in “International journal of current microbiology and applied sciences” A Pug with skin issues was successfully treated for mite and bacterial infections.
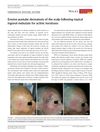 9 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
9 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Two elderly men developed scalp inflammation after using a gel for skin lesions, which healed with treatment except for some permanent hair loss.
 34 citations,
August 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
34 citations,
August 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Stress and emotional factors can worsen skin conditions by affecting the immune system.
 2 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Obesity may worsen hair loss in men and increase hirsutism in overweight or obese individuals, with weight loss recommended for treatment.

Hair loss can happen after severe H1N1 flu but usually grows back in 4 months.

PRP therapy effectively treats hair loss, wrinkles, scars, ulcers, and skin pigmentation disorders.
 7 citations,
May 2022 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
May 2022 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss is a frequent long-term effect of COVID-19, and oral minoxidil is the most common effective treatment.
77 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” TRPV3 in skin cells causes inflammation and cell death.
6 citations,
July 2015 in “JAAD Case Reports” Doxycycline can effectively treat hair loss caused by EGFR inhibitors.
 5 citations,
October 2016 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
5 citations,
October 2016 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” A man from Brazil had a rare case of leprosy on his scalp, which improved with treatment.























