 19 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
19 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology” New chemotherapy drugs cause skin side effects, but treatments like minocycline and tetracycline can help reduce them.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 7 citations,
November 2021 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
7 citations,
November 2021 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Skin side effects from cancer treatments can lead to changes in therapy and are common, with nail changes being the most frequent.
 7 citations,
October 2019 in “Annals of palliative medicine”
7 citations,
October 2019 in “Annals of palliative medicine” New targeted cancer drugs can cause skin side effects, and managing them requires patient education and timely care.
86 citations,
November 2020 in “Annals of Oncology” Early intervention and tailored management can reduce skin side effects from cancer treatments.
 27 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
27 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Zinc can be a helpful secondary treatment for certain skin conditions, but more research is needed to guide its use.
 18 citations,
December 1996 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
18 citations,
December 1996 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Chemotherapy and cytokine therapy can cause various skin reactions, including hair loss and hypersensitivity.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Targeted therapies for lung cancer are effective but require careful management of side effects to benefit patients.
 February 2022 in “JID Innovations”
February 2022 in “JID Innovations” The Virtual Magic Wand program successfully trained dermatologists in innovation, with most feeling capable of leading innovation teams and many starting companies.
2 citations,
September 2015 in “Türk pediatri arşivi : İstanbul çocuk kliniği dergisi” Valproic acid can very rarely cause nail separation, which usually gets better on its own after stopping the drug.
 15 citations,
December 2014 in “Dermatology and therapy”
15 citations,
December 2014 in “Dermatology and therapy” Sorafenib can cause facial acne-like eruptions, which improve after reducing the dose or stopping the drug.
 6 citations,
April 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
6 citations,
April 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Dermatologists are crucial for managing skin side effects in metastatic melanoma patients using vemurafenib and ipilimumab.
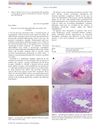 5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Sorafenib can cause delayed skin problems, so patients need careful monitoring.
 4 citations,
January 2018 in “Cancer treatment and research”
4 citations,
January 2018 in “Cancer treatment and research” The document concludes that systemic therapy is becoming more important in treating head and neck cancer, with new treatments showing promise.
 192 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
192 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause serious skin problems that need careful management.
 21 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
21 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology” New treatments for advanced skin cancer are improving patient outcomes, but drug resistance and finding the right treatment combinations are still big challenges.
 3 citations,
October 2003 in “Annals of Oncology”
3 citations,
October 2003 in “Annals of Oncology” A woman with low thyroid function did not lose her hair during chemotherapy, possibly because her hair follicles were less affected by the treatment.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Any drug can cause skin reactions, but antibiotics, NSAIDs, and psychotropic drugs are more common, with some reactions being life-threatening.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and treatment of follicular disorders are crucial, with specific treatments for conditions like acne, drug-induced eruptions, and rosacea.
 July 2008 in “Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal”
July 2008 in “Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal” New cancer treatments are more precise and less toxic, improving survival rates, but Asia faces challenges in adopting these advancements.
 76 citations,
August 2007 in “Supportive care in cancer”
76 citations,
August 2007 in “Supportive care in cancer” Chemotherapy often causes skin, nail, and hair side effects, significantly impacting quality of life.
 23 citations,
December 2004 in “Seminars in oncology”
23 citations,
December 2004 in “Seminars in oncology” Liposomal anthracyclines are effective and safer for treating multiple myeloma, especially in elderly patients.

PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin improves cancer treatment effectiveness and reduces side effects like heart damage and hair loss.
278 citations,
May 2013 in “Ca” Targeted anticancer therapies can cause severe side effects similar to traditional chemotherapy, but with different types.
10 citations,
February 2022 in “Epidemiologia” One-third of COVID-19 patients had long-term symptoms like hair loss and fatigue, with women, older individuals, blood group B, smokers, and those with more virus exposure at higher risk.
 2 citations,
September 2023 in “JMIR. Journal of medical internet research/Journal of medical internet research”
2 citations,
September 2023 in “JMIR. Journal of medical internet research/Journal of medical internet research” Machine learning can predict symptoms and quality of life in chronic skin disease patients using smartphone app data, and shows that app use varies with patient characteristics.
 9 citations,
July 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Brodalumab effectively treated a man's severe hand and foot psoriasis.
76 citations,
October 2000 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Follicular mucinosis can be an early sign of aggressive mycosis fungoides.
 165 citations,
February 2014 in “Phytotherapy Research”
165 citations,
February 2014 in “Phytotherapy Research” Myrtle has various health benefits and potential for medicine development.
 10 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
10 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Biotin supplements improved skin and hair problems in a girl with biotinidase deficiency.

























