 17 citations,
January 2010 in “PubMed”
17 citations,
January 2010 in “PubMed” Optimal storage solutions and effective additives are crucial for improving the survival of hair transplant grafts.
 81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Effective hair loss treatment in women requires correct diagnosis and can include medications like minoxidil, antiandrogens, and treatments for underlying conditions like PCOS.
 13 citations,
January 2012 in “International journal of trichology”
13 citations,
January 2012 in “International journal of trichology” The study found that hair fragility in Pili annulati may be caused by cavities and damage within the hair shafts.
1 citations,
November 2023 in “Cosmetics” Surfactants damage hair, but sealing the cuticle can prevent this.
 1 citations,
November 2002 in “Journal of dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2002 in “Journal of dermatology” The antibody created from BCC tissues reacts similarly to both BCC and hair follicles, suggesting BCC may come from hair follicle cells.
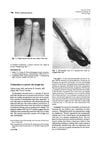 3 citations,
October 1990 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 1990 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Mechanical trauma like towel drying can cause knotted hair even in straight hair.
 11 citations,
May 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
May 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Using a blow dryer in a certain way can cause localized hair damage with bubble formation inside the hair.
27 citations,
September 1988 in “PubMed” Hair follicle shape determines hair type: curly, straight, or in-between.
 5 citations,
March 2017 in “Laser Physics Letters”
5 citations,
March 2017 in “Laser Physics Letters” Different scalp imaging methods are important for studying hair and scalp health and require more volunteers for better evaluation.
 33 citations,
January 2005 in “Dermatology”
33 citations,
January 2005 in “Dermatology” Trichoscan is a reliable method for measuring hair growth and monitoring treatment effectiveness in hair loss.
January 2020 in “Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society” Tiny lipid particles loaded with a hormone gather in hair follicles, which may help treat hair loss.
116 citations,
April 1986 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” Trichohyalin is a protein in hair follicles that helps form hair filaments.
January 2016 in “International journal of clinical pediatrics” Valproic acid may cause temporary hair changes like loss or thinning in children.
181 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of controlled release” Smaller nanoparticles improve minoxidil absorption through hair follicles.
 1 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” The document concludes that the trichogram is a useful tool for diagnosing hair loss and suggests semi-organ cultures for practical trichological research.
4 citations,
March 2016 in “Small ruminant research” Vicuña wool's quality is due to a high density of fine secondary hair follicles, and their skin glands may be used for communication.

New methods to classify curly hair types were developed based on shape and strength.
17 citations,
July 1984 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” The four patients have a unique type of ichthyosis affecting hair follicles.
13 citations,
December 1983 in “Canadian journal of zoology” Heterotypic cell contacts likely help hair matrix cells differentiate during mouse hair follicle development.
19 citations,
July 2004 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Her hair grew back normally after she stopped rubbing it.
50 citations,
December 2000 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” Hair follicles significantly enhance electroosmotic transport during iontophoresis.
Nanoparticles with caffeine can be used for slow, continuous hair growth stimulation.
 6 citations,
November 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
6 citations,
November 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair analysis is not good for assessing nutrition but can detect long-term heavy metal exposure.
 78 citations,
September 2008 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
78 citations,
September 2008 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” The document concludes that various clinical methods are used to assess ageing skin and the effectiveness of anti-ageing products.
 January 2024 in “Seven Editora eBooks”
January 2024 in “Seven Editora eBooks” Different techniques measure hair properties to ensure cosmetic products work.
 19 citations,
December 2013 in “European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics”
19 citations,
December 2013 in “European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics” Encapsulated Garcinia mangostana extract in cream penetrates skin better than other forms.
 1 citations,
September 2021 in “International journal of research - granthaalayah”
1 citations,
September 2021 in “International journal of research - granthaalayah” Human hair has bipolar electrical charges because of a gap in the hair follicle's electromagnetic field.
 58 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences”
58 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences” Multiphoton microscopy is a promising tool for detailed skin imaging and could improve patient care if its challenges are addressed.
49 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Careful light microscopy is crucial for detecting mild cases of pili annulati, which weakens hair and varies widely in expression.
2 citations,
July 2021 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Hair shaft disorders are diagnosed through examination and history, with general care and some treatments offering improvement.
















