Trichonodosis in a Patient with Straight Hair
October 1990
in “
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology
”
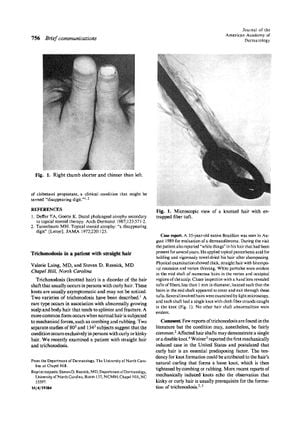
TLDR Mechanical trauma like towel drying can cause knotted hair even in straight hair.
The document described a case of trichonodosis (knotted hair) in a 35-year-old Brazilian man with straight hair, which was unusual since the condition typically occurred in individuals with curly or kinky hair. The patient had thick, straight hair with bitemporal recession and vertex thinning, and reported "white things" in his hair. Examination revealed tufts of fibers entrapped in the knots, likely caused by vigorous towel drying. This case suggested that mechanical trauma, such as towel drying, could induce trichonodosis even in straight hair, challenging the notion that curly hair is a prerequisite for the condition. The study emphasized the importance of clinical examination and light microscopy for diagnosing hair shaft abnormalities.



