 38 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell and Tissue Research”
38 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell and Tissue Research” The hair follicle infundibulum plays a key role in skin health and disease, and understanding it better could lead to new skin disease treatments.
 19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics”
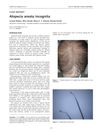
19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics” A young woman with a rare hair loss condition improved with steroid and biotin treatment.
 31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Minoxidil helps stabilize hair loss, increase density, and reduce shedding after hair transplant surgery.
[object Object]  January 2024 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences”
January 2024 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences” Homeopathic treatments can effectively manage hair loss and improve well-being.
 77 citations,
March 2021 in “Nature”
77 citations,
March 2021 in “Nature” Stress hormone corticosterone blocks a growth factor to slow down hair stem cell activity and hair growth.
 343 citations,
December 2008 in “Endocrine Reviews”
343 citations,
December 2008 in “Endocrine Reviews” Metformin helps with menstrual cycles and insulin levels in PCOS but is less effective for hair growth, diabetes prevention, and weight loss, and may improve fertility and reduce diabetes risk.
 19 citations,
January 2017 in “Stem Cells International”
19 citations,
January 2017 in “Stem Cells International” Adipose-derived stem cells show promise in treating skin conditions like vitiligo, alopecia, and nonhealing wounds.
 5 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
5 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Hair and skin healing involve complex cell interactions controlled by specific molecules and pathways, and hair follicle cells can help repair skin wounds.
19 citations,
July 2020 in “EBioMedicine” A gene variant increases the risk of a type of hair loss by affecting hair protein production.
 February 2009 in “Springer eBooks”
February 2009 in “Springer eBooks” Pregnancy can cause more body and scalp hair growth and make nails brittle, but these changes often revert after giving birth.
 7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions and is easy to diagnose, but rare types require careful evaluation.
 September 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
September 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Freezing gamma-irradiated amniotic fluid may help hair growth and speed up the growth phase.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A new treatment using AGED to modulate PPAR-γ shows promise for treating scarring hair loss by protecting and repairing hair follicle cells.
 24 citations,
December 2014 in “International Journal of Molecular Medicine”
24 citations,
December 2014 in “International Journal of Molecular Medicine” Eclipta alba extract helps increase hair growth and decrease hair loss-related protein in mice.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Macrophages are more involved in Lichen planopilaris than in Frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today”
100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today” Growth factors and cytokines are important for hair growth and could potentially treat hair loss, but more research is needed to overcome challenges before they can be used in treatments.
 16 citations,
October 2020 in “Lipids in Health and Disease”
16 citations,
October 2020 in “Lipids in Health and Disease” Leptin affects skin and hair health and may worsen some skin conditions, but more research is needed to understand its full impact.
[object Object]  58 citations,
February 2016 in “Scientific reports”
58 citations,
February 2016 in “Scientific reports” Blocking BACE1 and BACE2 enzymes causes hair color loss in mice.
 21 citations,
January 2020 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology”
21 citations,
January 2020 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology” Lack or blocking of SRD5a, a key component in hormone creation, can lead to conditions like pseudohermaphrodism and affect hair growth, bone mass, muscle strength, and reproductive health. More research is needed on its regulation from fertilization to adulthood.
 37 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
37 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking a protein called CXXC5 with a specific peptide can stimulate hair regrowth and new hair growth in wounds.
 103 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of Cell Biology”
103 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of Cell Biology” MicroRNA-214 is important for skin and hair growth because it affects the Wnt pathway.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Methods”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Methods” The document explains how to create detailed biological pathways using genomic data and tools, with examples of hair and breast development.
 271 citations,
March 1999 in “Developmental biology”
271 citations,
March 1999 in “Developmental biology” The research shows that a gene called Wnt3 affects hair growth and structure, causing short hair and balding when overactive.
 15 citations,
February 1999 in “The anatomical record”
15 citations,
February 1999 in “The anatomical record” Some mutant mice have hair with abnormal cross-linking, mainly in the cuticle, not affecting other hair parts.
 125 citations,
January 1999 in “Drugs”
125 citations,
January 1999 in “Drugs” Finasteride effectively treats baldness but may cause sexual side effects.
 23 citations,
January 2021 in “Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy”
23 citations,
January 2021 in “Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy” DHT stops hair regrowth in mice, similar to human hair loss.
 4 citations,
November 2017 in “Scientific Reports”
4 citations,
November 2017 in “Scientific Reports” The research provides a gene-based framework for hair biology, highlighting the Hippo pathway's importance and suggesting links between hair disorders, cancer pathways, and the immune system.
 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 45-year-old woman with autoimmune diseases experienced patchy hair loss due to alopecia areata, which has no cure but can be treated, with varying success.
4 citations,
March 2022 in “Pharmaceutics” Regenerative cellular therapies show promise for treating non-scarring hair loss but need more research.
29 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” P-cadherin is crucial for hair follicle pigmentation but not skin pigmentation.



























