 3 citations,
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Photodynamic therapy may not work for erythroplasia of Queyrat and could lead to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
[object Object]  19 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
19 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Acne lesions start with changes in hair follicles and increase in inflammation, suggesting a cycle that could affect treatment strategies.
 August 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Valproic acid, a common antiepileptic medication, can cause reversible hair loss in patients.
 53 citations,
May 1987 in “The Lancet”
53 citations,
May 1987 in “The Lancet” The document suggests a possible link between Crohn's disease and Johne's disease and calls for more research.
 109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” New treatments targeting specific genes show promise for treating keratin disorders.
 4 citations,
August 2011 in “Aktuelle Dermatologie”
4 citations,
August 2011 in “Aktuelle Dermatologie” Topical melatonin is a safe treatment that may reduce hair loss in people with androgenetic alopecia.
 1 citations,
November 2017
1 citations,
November 2017 The document concludes that while some organisms can regenerate body parts, mammals generally cannot, and cancer progression is complex, involving mutations rather than a strict stem cell hierarchy.
 6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology”
6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology” New oral testosterone formulations show potential for safer, effective hormone replacement in men with low testosterone.
 August 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Skin may help in getting rid of excess iron through the process of skin cell renewal.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Butyrate helps hair grow longer, improves hair cell health, increases pigment production, and boosts hair's natural defenses.
 14 citations,
May 2011 in “Drug Metabolism and Disposition”
14 citations,
May 2011 in “Drug Metabolism and Disposition” Ketoconazole increases finasteride's effectiveness and lifespan in the body.
143 citations,
May 2017 in “Nature cell biology” Wounded skin cells can revert to stem cells and help heal.
 1 citations,
October 2022 in “JCI insight”
1 citations,
October 2022 in “JCI insight” Deleting the BRD4 protein in certain skin cells causes hair loss and skin inflammation.
 39 citations,
November 2015 in “Nanomedicine”
39 citations,
November 2015 in “Nanomedicine” Improved Finasteride delivery for hair loss treatment.
 8 citations,
December 1981 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
December 1981 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that parathyroid diseases have a range of clinical features and outcomes, with some conditions being treatable and others having a high risk of mortality.
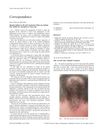 22 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
22 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” Orlistat might block the body's ability to absorb thyroid medication.
[object Object] 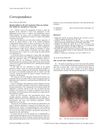 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 75 citations,
January 2009 in “International journal of trichology”
75 citations,
January 2009 in “International journal of trichology” Hair grays due to oxidative stress and fewer functioning melanocytes.
 59 citations,
February 1998 in “Chemico-Biological Interactions”
59 citations,
February 1998 in “Chemico-Biological Interactions” Minoxidil breakdown varies by enzymes, affecting hair loss treatment effectiveness.
15 citations,
September 2018 in “Hearing research” Rapamycin reduces age-related hearing cell loss in mice, but acarbose does not.
134 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental dermatology” Hair follicles are normally protected from the immune system, but when this protection fails, it can cause hair loss in alopecia areata.
 68 citations,
November 2011 in “The American journal of pathology”
68 citations,
November 2011 in “The American journal of pathology” Abnormal Hedgehog signaling in blood cancers may help tumors grow and resist chemotherapy, suggesting potential for targeted treatments.
 76 citations,
May 2011 in “Liver transplantation”
76 citations,
May 2011 in “Liver transplantation” Liver transplantation is a viable option for children with propionic acidemia, improving quality of life and diet, but does not remove all risks and long-term brain outcomes are uncertain.
 May 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
May 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” More research is needed to understand how testosterone is maintained in adult males.
 21 citations,
January 2020 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology”
21 citations,
January 2020 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology” Lack or blocking of SRD5a, a key component in hormone creation, can lead to conditions like pseudohermaphrodism and affect hair growth, bone mass, muscle strength, and reproductive health. More research is needed on its regulation from fertilization to adulthood.
 66 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Molecular Biology”
66 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Molecular Biology” The document concludes that for hair and feather growth, it's better to target the environment around stem cells than the cells themselves.
 14 citations,
August 2009 in “Cancer epidemiology”
14 citations,
August 2009 in “Cancer epidemiology” AHCC reduces hair loss and liver injury caused by chemotherapy in rodents.
 5 citations,
January 2020 in “Wiadomości lekarskie (Warsaw Poland)”
5 citations,
January 2020 in “Wiadomości lekarskie (Warsaw Poland)” Patients with both connective tissue disease and acid reflux are more likely to have certain symptoms and physical signs.
 3 citations,
August 2023 in “Drug safety”
3 citations,
August 2023 in “Drug safety” Proactive monitoring and management are essential to maximize the benefits of Trastuzumab Deruxtecan while minimizing serious side effects.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Medications for PCOS don't seem to raise heart disease risk.



























