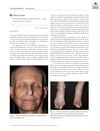
 March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Rothmund-Thomson syndrome type 2 can cause chronic, poorly healing wounds.
 1 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomedicines”
1 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomedicines” Understanding how acne develops in different diseases could lead to new treatments.
14 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A rare gene mutation causes skin fragility and itching without affecting hair or nails.
 2 citations,
August 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A specific mutation in the K25 gene causes a rare genetic disorder with curly hair at birth and later hair loss, along with dental issues.
 27 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
27 citations,
November 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The conclusion is that androgenetic alopecia and senescent alopecia have unique gene changes, suggesting different causes and potential treatments for these hair loss types.
 October 2011 in “Journal of dermatology”
October 2011 in “Journal of dermatology” A man with a rare skin condition and a new gene mutation developed high calcium levels due to his treatment.
 7 citations,
July 2005 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
7 citations,
July 2005 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The gene URB is more active in human hair growth cells and responds to a hair-related hormone.
 7 citations,
March 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
March 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Applying minoxidil can help improve hair growth in people with hair loss caused by LIPH gene mutations.
4 citations,
January 2018 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Hair transplantation successfully treated hair loss in a patient with Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome.
 32 citations,
August 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
32 citations,
August 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Early onset hair loss linked to genetics and androgen levels.
 June 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
June 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” UV radiation may cause DNA changes in skin, certain UVB therapy helps psoriasis, a new gene mutation is linked to mild piebaldism, different immune cells affect psoriasis, a drug promotes hair growth, and some cancer drugs could treat skin barrier issues.
 1 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
1 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The meeting presented new findings on hair stem cells, pigmentation, genetics, and modern hair treatment techniques.
 1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” A woman's hyperandrogenism was caused by a genetic mutation leading to non-classic adrenogenital syndrome.
November 2005 in “Hair transplant forum international” Genetic differences in hair loss can help improve diagnosis and treatment.
 2 citations,
October 2020 in “Annals of Oncology”
2 citations,
October 2020 in “Annals of Oncology” Men may be more vulnerable to severe COVID-19 due to genetic and hormonal factors, but more research is needed.
 88 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology”
88 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia are crucial for preventing serious health issues and improving patient outcomes.
 1 citations,
July 2021 in “Current Issues in Molecular Biology”
1 citations,
July 2021 in “Current Issues in Molecular Biology” Father's finasteride use may affect son's fertility and testicular function.
1 citations,
January 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Genetic testing is crucial for diagnosing and managing non-Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa.
 14 citations,
September 2018 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
14 citations,
September 2018 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” A boy's growth and immune problems were caused by a new mutation in the STAT5B gene.
 7 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
7 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Gene differences found in hair follicles linked to male baldness.
 2 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Differences in gene expression and methylation patterns found in AGA patients suggest potential targets for future treatments.
 4 citations,
May 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
4 citations,
May 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Platelet-rich plasma may help with wound healing, hair growth, and skin rejuvenation, but more research is needed to prove its effectiveness.
 7 citations,
January 2021 in “The journal of gene medicine”
7 citations,
January 2021 in “The journal of gene medicine” Certain genetic differences may affect how likely someone is to get COVID-19 and how severe it might be.
 52 citations,
May 2015 in “PLOS Genetics”
52 citations,
May 2015 in “PLOS Genetics” miR-22, a type of microRNA, controls hair growth and its overproduction can cause hair loss, while its absence can speed up hair growth.
 November 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
November 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Organ transplant recipients have a higher risk of skin cancer over time, atopic dermatitis skin shows unusual bacterial and fungal patterns, a new tool for measuring hidradenitis suppurativa severity was created, and gene expression changes in male baldness suggest new treatments.
 256 citations,
October 2013 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
256 citations,
October 2013 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Growing human skin cells in a 3D environment can stimulate new hair growth.
25 citations,
April 2017 in “PloS one” Certain genetic variations in the FST gene are linked to better wool quality in Chinese Merino sheep.
88 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking TRPV3 may help treat itch in dry skin conditions.
 38 citations,
April 2017 in “PLOS Genetics”
38 citations,
April 2017 in “PLOS Genetics” GRHL3 is important for controlling gene activity in skin cells during different stages of their development.
5 citations,
April 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A new therapy for a skin blistering condition has not been developed yet.























