 8 citations,
January 2016 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery”
8 citations,
January 2016 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery” PRGF treatment is safer and more effective for hair loss than topical minoxidil.
 115 citations,
June 2004 in “Pediatrics”
115 citations,
June 2004 in “Pediatrics” Children, especially teenagers, can get severe SARS-CoV infection with symptoms similar to adults, but they typically recover well with supportive care.
 58 citations,
March 2020 in “Scientific Reports”
58 citations,
March 2020 in “Scientific Reports” EGFR-TKIs can cause significant skin, nail, and organ side effects.
 11 citations,
February 2008 in “British journal of nursing”
11 citations,
February 2008 in “British journal of nursing” Idiopathic hirsutism causes excessive hair growth in women, can be treated with medication and hair removal, but cannot be fully reversed.
 August 2023 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2023 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” A substance called Cell-free fat extract can effectively treat common hair loss by increasing hair growth and density.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Different causes of beard hair loss have various treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures to stimulate hair growth.
 1 citations,
October 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
1 citations,
October 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Customized medications made through compounding can be beneficial for various skin conditions but require careful regulation and collaboration between doctors and pharmacists.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments targeting specific cells often cause skin, hair, and nail problems, affecting patients' lives and requiring careful management.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Lasers are less favored for hair transplant surgery but show promise for hair growth in controlled trials.
 11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology”
11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology” Acne and increased body hair in teenage girls are normal but severe cases may need hormone evaluation and treatment can prevent diabetes linked to PCO.
 April 2024 in “Frontiers in medicine”
April 2024 in “Frontiers in medicine” Alopecia Areata significantly lowers quality of life and current treatments are inadequate, highlighting a need for better therapies and standardized treatment protocols.
 13 citations,
January 2010 in “Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology”
13 citations,
January 2010 in “Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology” Understanding hair biology is key to developing better treatments for hair and scalp issues.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals” Natural products and phytochemicals may help with hair regrowth, but more research is needed.
 10 citations,
November 2022 in “Protein & Cell”
10 citations,
November 2022 in “Protein & Cell” Quercetin significantly helps hair growth by activating hair follicles and improving blood vessel formation around them.
 5 citations,
January 2001 in “Advances in protein chemistry”
5 citations,
January 2001 in “Advances in protein chemistry” 5α-reductase inhibitors help treat disorders caused by DHT and have potential for future therapies.
 65 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine”
65 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine” Plant extracts effectively reduce hair loss and increase growth, offering a safe alternative treatment.
 68 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine”
68 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine” Natural 5AR inhibitors effectively improve mild to moderate hair loss in men.
 1 citations,
August 2021 in “Педиатр”
1 citations,
August 2021 in “Педиатр” Endocrine diseases in children often cause skin changes like dryness, redness, acne, hair loss, and more.
 11 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research”
11 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research” Substance abuse can cause various skin problems, including marks from injections, sores, premature aging, and increased cancer risk.
 59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science”
59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science” Understanding how hair follicle stem cells work can help find new ways to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
 10 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
10 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Diabetes can lead to blindness and skin problems, and managing blood sugar and blood pressure is crucial to prevent these complications.
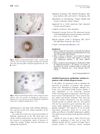 30 citations,
August 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
30 citations,
August 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Bimatoprost is safe but not effective for severe eyelash loss from alopecia areata, possibly helping those with less loss.
 24 citations,
January 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
24 citations,
January 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Some plants with flavonoids may help treat hair loss and promote hair growth.
 January 1998 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
January 1998 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Lasers are effective and safe for various medical treatments, including cancer, wound healing, and skin conditions.
 90 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy”
90 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy” Low-level laser therapy might help hair growth, but more research is needed.
 42 citations,
April 2012 in “Seminars in Oncology”
42 citations,
April 2012 in “Seminars in Oncology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin problems that need careful management to improve patient quality of life and treatment success.
 January 2011 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 2011 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Tretinoin gel is safe for sun exposure, but tacalcitol doesn't significantly improve non-segmental vitiligo.
 July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Nannochloropsis salina fermented oil may help treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and reducing oxidative stress.
 January 2009 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2009 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that treating skin conditions should include psychological care and a multidisciplinary approach is essential for effective management.
 5 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” High concentration Minoxidil and Carboxygas effectively treated resistant hair loss with no side effects.






























