 46 citations,
December 2003 in “Advances in neonatal care”
46 citations,
December 2003 in “Advances in neonatal care” Assessing newborn scalp hair can reveal important health information.
 2 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry”
2 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry” Neuronatin is found in specific cells within rat testis, hair follicles, tongue, and pancreas, suggesting it has various roles in tissue development and function.
 171 citations,
October 1990 in “Alcoholism/Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research”
171 citations,
October 1990 in “Alcoholism/Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research” The document concludes that the exact way alcohol causes harm to fetal development is unknown, but it significantly affects nutrient transport to the fetus and a safe level of alcohol during pregnancy is not determined.
 26 citations,
August 1971 in “Journal of Morphology”
26 citations,
August 1971 in “Journal of Morphology” Lizards can regrow their tail scales with the same structure, distribution, and gender-specific features as the original ones, and this unique ability is not seen in adult mammals.
 5 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Molecular Histology”
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Molecular Histology” Both main and alternative Wnt signaling are important for regrowing rodent whisker follicles.
 13 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
13 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Twist1 helps maintain important features of cells crucial for hair growth by working with Tcf4 and β-catenin.
 21 citations,
June 2016 in “Genesis”
21 citations,
June 2016 in “Genesis” Researchers identified specific genes that are important for mouse skin cell development and healing.
 August 2023 in “Micromachines”
August 2023 in “Micromachines” The new method can create hair follicle-like structures but not complete hair with roots and shafts, needing more improvement.
Tan sheep's unique fur traits are determined during the embryonic stage by specific genes.
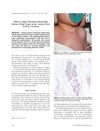 3 citations,
May 2013 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2013 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A newborn girl had a rare case of salivary gland tissue on her chest, which was safely removed.
 October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Immune cells are essential for early hair and skin development and healing.
January 2010 in “Chinese journal of clinical anatomy” Hair follicles in C57BL/6 mice develop rapidly from late embryonic stages to shortly after birth, with key growth and regeneration phases identified.
 March 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Twist2 is essential for proper skin healing and hair growth in developing mice.
 19 citations,
November 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
November 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The spiny mouse can regenerate its skin without scarring, which could help us learn how to heal human skin better.
 83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Skin development in mammals is controlled by key proteins and signals from underlying cells, involving stem cells for maintenance and repair.
 May 2024 in “Scientific reports”
May 2024 in “Scientific reports” Twist2 is essential for scarless skin healing and hair growth in mouse fetuses.
 43 citations,
August 2008 in “Regenerative Medicine”
43 citations,
August 2008 in “Regenerative Medicine” Scientists created early-stage hairs from mouse cells that grew into normal, pigmented hair when implanted into other mice.
 May 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Activating Wnt in skin cells controls the number of hair follicles by directing cell movement and fate.
 January 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
January 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Newly born mesenchymal cells quickly spread out in response to tissue tension during early development.
 84 citations,
December 2017 in “EMBO Reports”
84 citations,
December 2017 in “EMBO Reports” Circadian rhythms are crucial for stem cell function and tissue repair, and understanding them may improve aging and regeneration treatments.
 41 citations,
September 2005 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration”
41 citations,
September 2005 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration” Hydrogen peroxide can cause scars by changing healing processes and increasing certain protein levels.
 43 citations,
July 2019 in “Stem Cells International”
43 citations,
July 2019 in “Stem Cells International” Advancements in creating skin grafts with biomaterials and stem cells are promising, but more research is needed for clinical application.
 August 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Centrosomes are essential for healthy skin and hair growth, and their role is different from that of cilia.
71 citations,
November 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Edar signaling is crucial for proper hair follicle development and function.
 43 citations,
February 2013 in “Developmental dynamics”
43 citations,
February 2013 in “Developmental dynamics” Foxi3 expression in developing teeth and hair is controlled by the ectodysplasin pathway.
 66 citations,
May 2012 in “Scientific Reports”
66 citations,
May 2012 in “Scientific Reports” Scientists successfully created and transplanted bioengineered hair follicles that function like natural ones, suggesting a new treatment for hair loss.
 7 citations,
February 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports”
7 citations,
February 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports” Skin cells show flexibility in healing wounds and forming tumors, with potential for treating hair disorders and chronic ulcers.
 August 2023 in “Military Medical Research”
August 2023 in “Military Medical Research” Scientists have improved 3D models of human skin for research and medical uses, but still face challenges in perfectly replicating real skin.
 January 2024 in “ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering”
January 2024 in “ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering” A new method using a microfluidic device can prepare hair follicle germs efficiently for potential use in hair loss treatments.
 24 citations,
May 2019 in “PLOS ONE”
24 citations,
May 2019 in “PLOS ONE” The African spiny mouse can fully regenerate its muscle without scarring, unlike the common house mouse.



























