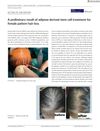
 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
 3 citations,
January 2022 in “Pharmaceutics”
3 citations,
January 2022 in “Pharmaceutics” Nanostructured delivery systems could potentially improve hair loss treatment by targeting drugs to hair follicles, reducing side effects and dosage, but the best size, charge, and materials for these systems need further investigation.
 14 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
14 citations,
January 2008 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Hormonal therapies like cyproterone acetate and spironolactone may help some women with hair loss, but finasteride 1mg is not useful, and the effectiveness of other treatments is still unclear.
 17 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology”
17 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia may affect nails and could be a type of lichen planus, treatable with certain medications.
January 2023 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The new 5% minoxidil foam is as effective and safe as Rogaine® for treating hair loss in Chinese men.
 January 2015 in “프로그램북(구 초록집)”
January 2015 in “프로그램북(구 초록집)” Dutasteride is effective and safe for treating common hair loss, and it's more potent than finasteride, leading to better hair growth and thickness.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Only minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved for hair loss, with other treatments available but less effective or with side effects.
 15 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
15 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Minoxidil and finasteride work best for hair loss; more research needed.
May 2018 in “Hair transplant forum international” Topical finasteride promotes hair growth with minimal side effects but needs more research for women and optimal use.
21 citations,
March 2018 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors may help stabilize or slow down hair loss in some frontal fibrosing alopecia patients, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness and safety.
 14 citations,
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
14 citations,
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” 10% minoxidil solution better promotes hair growth and reduces hair loss without significant side effects.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” AGA is a common hair loss disorder, and early diagnosis and treatment with minoxidil or finasteride can help reduce emotional distress.
 September 2023 in “Authorea (Authorea)”
September 2023 in “Authorea (Authorea)” Certain peptides, caffeine, taurine, and an iron complex may improve hair regrowth when used with minoxidil and finasteride for hair loss.
 13 citations,
September 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
13 citations,
September 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” PRP therapy and minoxidil combo works best for male hair loss.
 12 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
12 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) can promote new hair growth and increase hair density, but its effectiveness varies depending on the type of hair loss.
 August 2021 in “Research, Society and Development”
August 2021 in “Research, Society and Development” Minoxidil slightly increased hair volume more than Finasterida, but both reduced hair loss similarly.
 54 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
54 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Low level laser therapy works best for hair loss, followed by PRP, finasteride, and minoxidil.
 8 citations,
October 2020 in “Pharmaceutics”
8 citations,
October 2020 in “Pharmaceutics” Dutasteride-loaded nanoparticles coated with Lauric Acid-Chitosan show promise for treating hair loss due to their controlled release, low toxicity, and potential to stimulate hair growth.
 49 citations,
February 2019 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
49 citations,
February 2019 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” Use "female pattern hair loss" term, assess androgen excess, treat with minoxidil and other medications if needed.

Most American men experience hair loss by age 50, with limited effective treatments available and new options not expected soon.
 January 2025 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Combining oral minoxidil and bicalutamide may help improve hair growth in adolescent girls.
 January 2008 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2008 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Hormonal therapy like cyproterone acetate and spironolactone may help female hair loss, but more research is needed, especially for pre-menopausal women.
January 2022 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Oral minoxidil is a safe and effective treatment for patterned hair loss.
 2 citations,
October 2020 in “The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology”
2 citations,
October 2020 in “The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology” The herbal mix (Biochanin A, Acetyl tetrapeptide-3, and Ginseng Extracts) and the 3% Minoxidil solution are equally effective in treating hair loss, but the herbal mix has fewer side effects.
 23 citations,
December 2013 in “Regenerative Medicine”
23 citations,
December 2013 in “Regenerative Medicine” Hair follicle culture helps develop new treatments for hair loss.
August 2024 in “Cosmetics” Personalized treatments for hair loss are becoming more effective by using genetic information.
11 citations,
March 2021 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Treating hair loss in both men and women is effective and improves quality of life.
 15 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
15 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hair aging and loss are caused by genetics, hormones, environment, and grooming, with treatments like minoxidil effective for certain types of hair loss.
 6 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hair aging is inevitable, but using the right hair care products can help maintain hair health.
 121 citations,
May 2009 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology”
121 citations,
May 2009 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” Eclipta alba extract may help hair grow similarly to Minoxidil.
























