 July 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
July 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” Diphenylcyclopropenone is more effective and has fewer side effects than dinitrochlorobenzene for treating alopecia areata.
 June 2019 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
June 2019 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Alopecia in patients with epidermolysis bullosa varies in severity and is often caused by skin blistering or trauma.
[object Object]  January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Low-dose isotretinoin is as effective as conventional doses for acne and has fewer side effects.
February 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Combining microneedling with either vitamin D3 or bimatoprost improves hair regrowth more than microneedling alone.
 January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Genetic testing is crucial for diagnosing rare hair loss disorders.
 April 2023 in “Our Dermatology Online”
April 2023 in “Our Dermatology Online” Trichoscopy is effective in diagnosing trichotillomania by showing specific hair patterns.
 February 2021 in “Cureus”
February 2021 in “Cureus” A woman's hair loss was initially misdiagnosed as scarring hair loss but was actually a treatable autoimmune hair loss.
13 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in oncology” Reflectance confocal microscopy reliably identifies skin cancer features like horizontal skin tissue sections.
 August 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
August 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Higher concentration of botulinum toxin A is safe and effective for treating hair loss in men and women.
 July 2023 in “Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal”
July 2023 in “Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and manage hair and scalp disorders in children.
 January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology” A woman lost all her hair in one day, was diagnosed with a rare type of hair loss, and regrew it in 12 weeks with treatment.
 18 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
18 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Platelet-rich plasma shows potential for hair loss and skin rejuvenation but needs more research for widespread use.
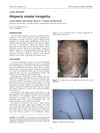 December 2007 in “CRC Press eBooks”
December 2007 in “CRC Press eBooks” Alopecia areata incognita causes widespread hair loss without patches and needs a scalp biopsy for diagnosis.
 21 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
21 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Vemurafenib therapy can cause hair loss, but clobetasol propionate foam can help regrow hair.
 14 citations,
December 2010 in “Dermatologica Sinica”
14 citations,
December 2010 in “Dermatologica Sinica” New treatments for hair loss show promise, but more development is needed, especially for tough cases.
 3 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology” Scalp biopsies help tell apart androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata.
 May 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
May 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” 5% topical minoxidil effectively treated a boy's congenital triangular alopecia without side effects.
 March 2022 in “Nepal Journal of Dermatology Venereology & Leprology”
March 2022 in “Nepal Journal of Dermatology Venereology & Leprology” Methotrexate with steroids is slightly more effective than azathioprine with steroids for treating severe alopecia areata.
 45 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
45 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” A systematic approach is crucial for managing hair loss in women.
 34 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
34 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Combining low-level light therapy and minoxidil 5% is more effective for female hair loss than using either treatment alone.
 24 citations,
January 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
24 citations,
January 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Diffuse alopecia areata involves more inflammation and higher allergy-related antibodies than patchy types.
 23 citations,
June 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
23 citations,
June 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is a low-risk treatment for Androgenic Alopecia (AGA) that generally improves hair count or density, but more research is needed for optimization.
 17 citations,
November 2018 in “Dermatology”
17 citations,
November 2018 in “Dermatology” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia had facial bumps, with Hispanic/Latino and premenopausal women being more affected, suggesting a more severe condition.
 10 citations,
May 2021 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery”
10 citations,
May 2021 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery” Coenzyme Q10 vesicular formulations can potentially treat androgenic alopecia by promoting hair growth and thickness.
 6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Different hair loss types need accurate diagnosis for proper treatment.
 1 citations,
December 2017 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
1 citations,
December 2017 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Frontal fibrosing alopecia can mimic traction alopecia but has distinct features like facial papules and eyebrow thinning.
 January 2024 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
January 2024 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Male gender and family history predict alopecia areata recurrence.
 June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” The Middle East and Africa need better data, treatment consensus, and support for Alopecia Areata.
 205 citations,
April 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
205 citations,
April 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Platelet-rich plasma treatment significantly increased hair regrowth and decreased discomfort in alopecia patients, making it a potentially better and safer treatment option.
[object Object]  62 citations,
January 2013 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
62 citations,
January 2013 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Low iron and vitamin D levels are linked to hair loss in women.



























