 6 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
6 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Epimedium extract helps increase skin pigmentation and could be a new treatment for conditions with reduced pigmentation.
 291 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal”
291 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal” Lichen Planus is a less common condition affecting skin and mucous membranes, with various types and associated risk factors, challenging to diagnose, significantly impacts life quality, and may have a risk of cancerous changes in oral lesions.
 November 2023 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology”
November 2023 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology” Hair aging is caused by stress, hormones, inflammation, and DNA damage affecting hair growth and color.
 May 2024 in “European Journal of Immunology”
May 2024 in “European Journal of Immunology” Vitamin B5 and coenzyme A may help regulate the immune system and could improve treatments for chronic diseases and cancer.
 54 citations,
August 2019 in “Bioscience trends”
54 citations,
August 2019 in “Bioscience trends” Stem cells help repair tissue mainly by releasing beneficial substances, not by replacing damaged cells.
 56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
 January 2023 in “Applied sciences”
January 2023 in “Applied sciences” Gefitinib and Sasam-Kyeongokgo together significantly reduce cancer growth and improve immune response in mice.
 11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology”
11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology” Men are more likely to have severe respiratory viral infections like COVID-19 due to hormonal and genetic differences, while women generally have stronger immune responses.
 185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews”
185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss due to the immune system attacking hair follicles, often influenced by genetics and stress.
 57 citations,
March 2019 in “Immunity”
57 citations,
March 2019 in “Immunity” The document concludes that the skin's immune system is complex, involving interactions with hair follicles, nerves, and microbes, and can protect or cause disease, offering targets for new treatments.
 48 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
48 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Hair follicles offer promising targets for delivering drugs to treat hair and skin conditions.
353 citations,
July 2015 in “Molecular immunology” Porcine skin is very similar to human skin, making it a useful model for research.
 30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” New treatments targeting immune pathways show promise for severe hair loss but need more research for safety and effectiveness.
 16 citations,
March 2018 in “Seminars in Oncology”
16 citations,
March 2018 in “Seminars in Oncology” The document concludes that pregnancy and cancer share immune evasion tactics, but more research is needed before using checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in pregnant cancer patients to avoid harm to the placenta.
 34 citations,
October 2017 in “Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria”
34 citations,
October 2017 in “Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria” Alopecia Areata is a complex, unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited treatment options and a significant psychological impact.
 May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Tofacitinib is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.
6 citations,
March 2020 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” CTLA4 gene variants are not linked to alopecia areata in Monterrey's Mexican population.
 141 citations,
August 2018 in “Nature Reviews Microbiology”
141 citations,
August 2018 in “Nature Reviews Microbiology” Some viruses can cause cancer by changing cell processes and avoiding the immune system; vaccines and targeted treatments help reduce these cancers.
37 citations,
November 2017 in “Medical Sciences” Melanoma's complexity requires personalized treatments due to key genetic mutations and tumor-initiating cells.
 June 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
June 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Tofacitinib regrew hair in a man with total hair loss but raised cytokine levels, needing more research on possible side effects.
 20 citations,
December 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
20 citations,
December 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Blocking IL-12/IL-23 does not help with hair loss in alopecia areata for mice or humans.

Alopecia areata patients have higher levels of certain immune receptors, suggesting new treatment possibilities.
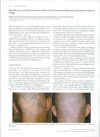 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 25 citations,
October 2019 in “JAAD Case Reports”
25 citations,
October 2019 in “JAAD Case Reports” Baricitinib helped a woman with severe hair loss regrow almost all her hair without side effects.
 3 citations,
July 2021 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health”
3 citations,
July 2021 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health” Two patients developed complete hair loss after Alemtuzumab treatment for MS, with no regrowth after two years.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
 23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Apremilast did not work for treating severe alopecia areata.
 59 citations,
February 2021 in “Advanced Functional Materials”
59 citations,
February 2021 in “Advanced Functional Materials” The silk fibroin-based hydrogel shows promise for treating melanoma and healing infected wounds by killing tumor cells and bacteria, and supporting skin recovery.
98 citations,
March 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Damaging mutations in NFKB2 cause a severe and distinct form of primary immunodeficiency with early-onset and often ACTH-deficiency.
 March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” A girl with severe hair loss saw hair regrowth after using cannabis.


























