 29 citations,
September 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
29 citations,
September 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The document concludes that freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma shows promise for medical use but requires standardization and further research.
 16 citations,
November 2019 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
16 citations,
November 2019 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Platelet-rich plasma is most effective for hair loss treatment and shows promise for skin healing and rejuvenation, but more standardized research is needed.
 16 citations,
November 2011 in “PubMed”
16 citations,
November 2011 in “PubMed” The treatment improved hair growth in people with male pattern baldness.
 13 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine”
13 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine” Traditional and complementary medicine may help with skin conditions, but more high-quality research is needed.
 2 citations,
August 2023 in “Life”
2 citations,
August 2023 in “Life” Bioinspired polymers are promising for advanced medical treatments and tissue repair.
 August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Human skin xenografting could improve our understanding of skin development, renewal, and healing.
 April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Bacteria can help skin regenerate through a process called IL-1β signaling.
 152 citations,
December 2007 in “Gender Medicine”
152 citations,
December 2007 in “Gender Medicine” Male and female skin differ due to hormones, affecting conditions like hair loss, acne, and skin cancer, and suggesting a need for gender-specific treatments.
 25 citations,
August 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
25 citations,
August 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Fractional lasers seem effective and safe for treating hair loss, but more research is needed to find the best treatment methods.
 79 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
79 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Platelet-rich plasma may have some benefits in dermatology, but there's not enough evidence to widely recommend its use.
 2 citations,
June 2023 in “Gels”
2 citations,
June 2023 in “Gels” Injectable hydrogels are becoming increasingly useful in medicine for drug delivery and tissue repair.
 19 citations,
August 2019 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery”
19 citations,
August 2019 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery” Platelet-rich plasma is beneficial in various plastic surgery applications, but more research is needed to standardize its use.
 17 citations,
June 2021 in “Molecules”
17 citations,
June 2021 in “Molecules” Melatonin-loaded nanocarriers improve melatonin delivery and effectiveness for various medical treatments.
 5 citations,
August 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
5 citations,
August 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using fat-derived stem cells with the drug meglumine antimoniate can help control skin disease and reduce parasites in mice with leishmaniasis.
 5 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
5 citations,
January 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Caffeine may benefit skin and hair health but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in dermatology.
 4 citations,
December 2014 in “PubMed”
4 citations,
December 2014 in “PubMed” Pre-operative hormone treatment for hypospadias surgery might improve outcomes, but more research is needed to confirm.
 May 2024 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
May 2024 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Applying DMG-Na to the skin increases blood flow and may help with skin conditions.
 36 citations,
December 2012 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
36 citations,
December 2012 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Injecting platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can increase hair growth rate and density in male pattern baldness.
67 citations,
May 2016 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Peptides, proteins, and growth factors in skincare show promise for improving skin health.
1 citations,
April 2024 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology” Microneedles combined with conventional therapies show promise in treating alopecia areata.
 36 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of Controlled Release”
36 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of Controlled Release” Genetically-altered adult stem cells can help in wound healing and are becoming crucial in regenerative medicine and drug design.
 141 citations,
August 2017 in “Developmental Dynamics”
141 citations,
August 2017 in “Developmental Dynamics” The document concludes that a better understanding of cell changes during wound healing could improve treatments for chronic wounds and other conditions.
 113 citations,
December 2000 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
113 citations,
December 2000 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” KGF and activin are crucial for skin healing and repair.
 26 citations,
January 1994 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
26 citations,
January 1994 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Artificial skin is improving wound healing and shows potential for treating different types of wounds.
 21 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery”
21 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery” Negative pressure wound therapy is effective for skin grafts in cats.
 14 citations,
February 2020 in “Stem Cells International”
14 citations,
February 2020 in “Stem Cells International” Umbilical cord cells safely improve healing in long-term nonhealing wounds better than a placebo.
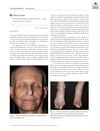 March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Rothmund-Thomson syndrome type 2 can cause chronic, poorly healing wounds.
 1160 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Reviews”
1160 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Reviews” The document concludes that better targeted treatments are needed for wound healing, and single-cell technologies may improve cell-based therapies.
 359 citations,
January 2015 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
359 citations,
January 2015 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Hair growth phase and certain genes can speed up wound healing, while an inflammatory mediator can slow down new hair growth after a wound. Understanding these factors can improve tissue regeneration during wound healing.
 204 citations,
October 1999 in “EMBO journal”
204 citations,
October 1999 in “EMBO journal” Overexpression of activin A in mice skin causes skin thickening, fibrosis, and improved wound healing.




























