 28 citations,
January 2017 in “Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems”
28 citations,
January 2017 in “Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems” Nanomaterials in biomedicine can improve treatments but may have risks like toxicity, needing more safety research.
 9 citations,
October 2017 in “Translational pediatrics”
9 citations,
October 2017 in “Translational pediatrics” Pediatric endocrinologists should provide early fertility counseling and preservation options to young patients at risk of infertility.
 24 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology”
24 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology” The spiny mouse is a unique menstruating rodent that can help us understand menstruation and reproductive disorders.
 July 2015 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
July 2015 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” The most common skin diseases found were contact dermatitis, scabies, fungal infections, urticaria, and acne, highlighting the need for better public health policies and awareness.
 April 2024 in “Journal of translational medicine”
April 2024 in “Journal of translational medicine” Melanocytes are important for normal body functions and have potential uses in regenerative medicine and disease treatment.
 85 citations,
July 2002 in “Pigment Cell Research”
85 citations,
July 2002 in “Pigment Cell Research” The article concludes that while we understand a lot about how melanocytes age and how this can prevent cancer, there are still unanswered questions about certain pathways and genes involved.
 70 citations,
March 2016 in “Urologic Clinics of North America”
70 citations,
March 2016 in “Urologic Clinics of North America” The document explains how the male reproductive system works, its role in making testosterone, and how conditions like obesity can disrupt it, leading to low testosterone and fertility issues.
July 2011 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology” A 15-year-old girl has a skin condition causing blisters on her feet, likely inherited from her family.
 October 2024 in “Andrology”
October 2024 in “Andrology” Paternal drug exposure can harm fertility, pregnancy outcomes, and offspring health, with specific drugs linked to various reproductive issues.
 1 citations,
March 2019 in “KnE life sciences”
1 citations,
March 2019 in “KnE life sciences” HDPCM treatment healed a baby's congenital skin defect caused by varicella infection.
 December 2024 in “Kırıkkale Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi”
December 2024 in “Kırıkkale Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi” Chromosomal microarray analysis is important for diagnosing rare genetic variations and guiding treatment.
Deleting the MAD2L1 gene is tolerated in certain mouse cancer models.
 60 citations,
August 2008 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
60 citations,
August 2008 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” A position effect on the TRPS1 gene causes excessive hair growth in humans and mice.
Deleting the MAD2L1 gene in mice led to rapid tumor growth despite chromosomal instability.
 March 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is relatively common in children, has a variable course, and shows different responses to treatment; thyroid testing is recommended for those affected.
 May 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology”
May 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology” Mother and son diagnosed with a rare genetic hair loss condition with no effective treatment.
 2 citations,
July 2016 in “Pharmacopsychiatry”
2 citations,
July 2016 in “Pharmacopsychiatry” A person with Turner Syndrome showed severe schizophrenia that didn't respond to treatment and had brain shrinkage.
 26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New gene identification techniques have improved the understanding and classification of inherited hair disorders.
37 citations,
November 2017 in “Medical Sciences” Melanoma's complexity requires personalized treatments due to key genetic mutations and tumor-initiating cells.
 3 citations,
January 2023 in “Science advances”
3 citations,
January 2023 in “Science advances” The enzymes Tet2 and Tet3 are important for skin cell development and hair growth.
63 citations,
April 2005 in “Mechanisms of development” Mice with too much Claudin-6 have skin barrier problems and abnormal hair growth.
 2 citations,
August 2014 in “Archivos argentinos de pediatría”
2 citations,
August 2014 in “Archivos argentinos de pediatría” A 6-year-old girl with Turner syndrome also had psoriasis, alopecia areata, and trachyonychia.
 June 2008 in “Springer eBooks”
June 2008 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that permanent hair loss conditions are complex, require early specific treatments, and "secondary permanent alopecias" might be a more accurate term than "secondary cicatricial alopecia."
 7 citations,
July 1975 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
7 citations,
July 1975 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” A patient with Rothmund-Thomson syndrome showed skin changes, hair loss, and dental defects but no cataracts or skeletal issues.
10 citations,
November 2018 in “The Italian Journal of Pediatrics/Italian journal of pediatrics” Early diagnosis of Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 is crucial for treatment and was achieved through clinical examination and family history.
188 citations,
June 1998 in “Molecular cell” Researchers created a mouse with the same mutation as humans with trichothiodystrophy, showing similar symptoms and confirming the condition is due to defects in DNA repair and gene activity.
 4 citations,
December 2020 in “Mammalian genome”
4 citations,
December 2020 in “Mammalian genome” Harlequin mutant mice have hair loss due to low AIF protein levels and retroviral element activity.
 25 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
25 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” Mutations in the androgen receptor gene cause Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, affecting sexual development.
 7 citations,
May 2019 in “European Journal of Human Genetics”
7 citations,
May 2019 in “European Journal of Human Genetics” BMP4-related anomalies can cause a wide range of eye, brain, and hand/foot problems, and new cases show this variability.
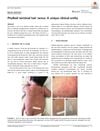 August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A baby had a unique skin condition with a pale patch and surrounding dark hairs, not linked to other health issues.























