
The woman was diagnosed with lichen sclerosus, a rare skin condition, after initial misdiagnosis and ineffective treatments.
 January 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Propylthiouracil, a thyroid medication, can cause skin blood clots and immune-related blood vessel inflammation.
 7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stopping imipramine reduced the woman's hair loss.
 391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.
75 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Alopecia areata can be triggered by specific immune cells without genetic or environmental factors.
 49 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
49 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Thyroid function affects skin health, with a complex interaction between the two.
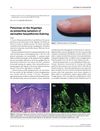 30 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
30 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Red spots on fingertips can be a sign of a skin condition linked to gluten sensitivity, treatable with a gluten-free diet.
 25 citations,
July 1994 in “Archives of Dermatology”
25 citations,
July 1994 in “Archives of Dermatology” A man's skin condition, pemphigus vulgaris, came back after he was treated with interleukin 2 for cancer.
 6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Women with alopecia may have a higher chance of getting thyroid cancer.
 3 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
3 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Some people with primary cicatricial alopecia also have inflammatory bowel disease, suggesting a possible connection.
 1 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Activating STAT5 in the skin's dermal papilla is key for starting hair growth, regenerating hair follicles, and healing wounds.
 1 citations,
January 2000 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2000 in “Springer eBooks” Pregnancy can cause various skin changes and diseases, requiring careful treatment to protect the baby.
 1 citations,
October 1971 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
October 1971 in “The BMJ” The document suggests that hair loss after stopping birth control may be similar to post-pregnancy hair loss and could recur with future pregnancies.
 January 2016 in “Journal of The Korean Medical Association”
January 2016 in “Journal of The Korean Medical Association” The document says how to diagnose and treat hair loss from alopecia areata, but there's no cure and treatments vary.
 January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition that often starts before age 30 and can affect various body parts, with unpredictable hair regrowth chances.
 January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair transplantation is a treatment for hair loss mainly caused by genetics, with various techniques and potential complications, and results visible after 8-12 months.

Alopecia areata often starts around age 23, can be permanent in 30% of cases, and treatments are usually temporary.
 81 citations,
July 2011 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
81 citations,
July 2011 in “Lasers in Medical Science” The Lexington LaserComb helped regrow hair in mice with a condition similar to human hair loss.
 56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
 20 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
20 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Hair diseases can have psychological effects and should be treated with a combination of psychosomatic care, therapy, and medication.
 19 citations,
May 2004 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
19 citations,
May 2004 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The research found that a specific gene mutation causes fewer hair follicles and disrupted hair growth cycles, leading to thin and short hair in people with Hypotrichosis with Juvenile Macular Dystrophy.
 19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Horizontal scalp biopsy sections are better for diagnosing alopecia areata, showing fewer hair follicles and more miniaturized hairs.
 2 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
2 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Thyroid problems are linked to various skin issues, and checking thyroid health is important for people with certain skin conditions.
 February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences”
February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences” No cure exists for alopecia areata, and treatments are personalized.
 114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety”
114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause skin, nail, and hair problems, which are important for healthcare professionals to recognize and report.
 105 citations,
September 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
105 citations,
September 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Recombinant cytokine therapy can cause skin reactions ranging from mild to severe.
 89 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
89 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia areata is likely caused by a combination of genetic factors and immune system dysfunction, and may represent different diseases with various causes.
 77 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
77 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Environmental factors, hormones, nutrition, and stress all significantly affect skin health and aging.
 63 citations,
May 2017 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
63 citations,
May 2017 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” People with alopecia areata often have lower levels of vitamin D, zinc, and folate, but more research is needed to understand if supplements can help treat it.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.





























