 6 citations,
November 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
6 citations,
November 1988 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair analysis is not good for assessing nutrition but can detect long-term heavy metal exposure.
 19 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research”
19 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research” The main causes of diffuse hair loss in women are telogen effluvium and androgenetic alopecia, often related to stress and iron deficiency.

Modern skin cancer treatments can cause skin side effects and hair loss, affecting patients' quality of life.
 January 2020 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2020 in “Elsevier eBooks” Plant-based chemicals may help hair growth and prevent hair loss but need more research to compete with current treatments.
 6 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of dermatology” Immune checkpoint inhibitors used in cancer therapy can cause hair loss, and understanding this can help manage the side effect.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Only minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved for hair loss, with other treatments available but less effective or with side effects.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cell reconstitution after thymus transplantation can cause hair whitening and loss.
 May 2024 in “Deleted Journal”
May 2024 in “Deleted Journal” Cancer treatments can cause hair loss, but it is often reversible and can be managed with scalp cooling and support.
 179 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
179 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Cancer treatments targeting specific cells and the immune system can cause skin, mouth, hair, and nail problems, affecting patients' quality of life and treatment adherence.
 62 citations,
January 2010 in “Hormone research in paediatrics”
62 citations,
January 2010 in “Hormone research in paediatrics” Genetic screening is crucial for accurately diagnosing APS-1 due to its varied symptoms.
 53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cancer treatments often cause hair disorders, significantly affecting patients' quality of life, and better management methods are needed.
 47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology”
47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” A new mutation in the STING protein causes a range of symptoms and its severity may be affected by other genetic variations; treatment with a specific inhibitor showed improvement in one patient.
 14 citations,
February 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
14 citations,
February 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Immune checkpoint inhibitors can cause skin issues but are linked to better cancer outcomes.
 11 citations,
July 2014 in “Gene”
11 citations,
July 2014 in “Gene” The S250C variant in a gene may cause autoimmunity and immunodeficiency by impairing protein function.
 4 citations,
November 2021 in “Cancers”
4 citations,
November 2021 in “Cancers” The document concludes that understanding and managing hair loss in cancer patients is important, and more research is needed for better treatments.
 1 citations,
March 2019 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
1 citations,
March 2019 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” New cancer treatments are less harmful to hair but can still cause hair loss, color, shape, and growth changes.
 10 citations,
June 2016 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration”
10 citations,
June 2016 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration” The microenvironment, especially mechanical forces, plays a crucial role in hair growth and could lead to new treatments for hair loss.
 46 citations,
January 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
46 citations,
January 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with late-stage HIV-1 often experience a specific type of hair loss linked to multiple factors, including nutritional issues and immune responses.
 3 citations,
February 2013 in “Bangladesh Journal of Medicine”
3 citations,
February 2013 in “Bangladesh Journal of Medicine” Low iron levels are linked to hair loss in women.
 27 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of optometry”
27 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of optometry” Eyelashes protect the eyes, but more research is needed to understand how.
 1 citations,
January 2022 in “Updates in clinical dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2022 in “Updates in clinical dermatology” Some drugs can cause changes to your hair.
 222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
 182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some treatments can help with a hair loss condition called alopecia areata, but none ensure lasting results; choices depend on the person, with JAK inhibitors showing promise for severe cases.
 41 citations,
September 2018 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
41 citations,
September 2018 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” No systemic treatment for alopecia areata has strong evidence of effectiveness.
 24 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology”
24 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in patients with alopecia, with few side effects.
17 citations,
November 2009 in “Dermato-endocrinology” Medium-dose prednisolone pulse therapy is effective and safe for multifocal alopecia areata but not for more severe forms.
 14 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
14 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” Some people with severe, long-lasting baldness responded well to a specific combination treatment.
 2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Early onset, severe types, nail changes, family history, and body hair loss worsen alopecia areata prognosis; sticking to treatment helps.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical and medical investigations”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical and medical investigations” Herbal lotions are effective for severe hair loss, with a 64.8% success rate, but relapse is common and long-term management requires allergen control and possible corticosteroid use.
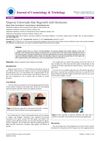 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.





























