 2 citations,
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology”
2 citations,
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology” Yellow dots and short vellus hairs are the most common signs of Alopecia Areata (AA), and trichoscopy can help diagnose AA and track treatment progress.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne is linked to inflammation and insulin resistance, and is associated with various syndromes that require different treatments.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “Experimental dermatology”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “Experimental dermatology” New imaging techniques can assess and track changes in mouse acne without harm, aiding treatment choices.
 51 citations,
January 2006 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration”
51 citations,
January 2006 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration” MRL/MpJ mice's skin wounds heal with scars, unlike their ear wounds which can regenerate.
 141 citations,
September 2016 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
141 citations,
September 2016 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Taxane chemotherapy can cause skin, hair, and nail side effects, which are often under-reported and can affect patient quality of life.
 22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that correct diagnosis of alopecia types is crucial, scalp biopsies are important, and more research is needed.
 23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” The study concluded that AAI and DAA are forms of the same disease, with different symptoms in men and women, and that corticosteroid treatment is effective.
 12 citations,
August 2022 in “Biochemical Journal”
12 citations,
August 2022 in “Biochemical Journal” Different types of cell death affect skin health and inflammation, and understanding them could improve treatments for skin diseases.
 31 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in Oncology”
31 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in Oncology” Photobiomodulation therapy helps manage cancer treatment side effects but needs more research for optimization.
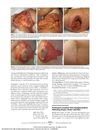 3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology” Herpes zoster infection can cause permanent hair color change in the affected area.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Faulty inflammasome activation may lead to autoimmune skin diseases and could be a target for new treatments.
 47 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
47 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that understanding and treating hair loss requires recognizing its various types and using appropriate diagnostic tools and treatments.
 May 1993 in “Current problems in dermatology”
May 1993 in “Current problems in dermatology” Skin symptoms are important for diagnosing infections in children.
 14 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
14 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The document concludes that new methods improve the accuracy of diagnosing scalp alopecia and challenges the old way of classifying it.
37 citations,
September 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A man with scalp and neck skin issues improved after a year of oral isotretinoin.
 20 citations,
June 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
20 citations,
June 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using stem cells from fat tissue can significantly improve wound healing in dogs.
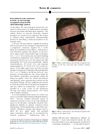 2 citations,
November 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
2 citations,
November 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Drinking kava tea can cause a skin reaction with red, swollen bumps, which may improve with steroids.
 43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Recognizing the different stages of alopecia areata is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Various drugs caused different skin reactions, including allergic and inflammatory responses.
 158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology”
158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology” Some people with pattern hair loss may also have scalp inflammation and scarring similar to lichen planopilaris.
 7 citations,
August 2018 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
7 citations,
August 2018 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Researchers found a new early sign of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia that could help avoid misdiagnosis.
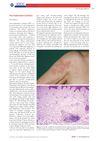 October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Post-implantation erythema is a red skin condition after medical device implantation that sometimes goes away on its own.
 72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Anti-TNF therapy can cause a unique type of hair loss that may get better with topical treatments without stopping the therapy.
 33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” A fungal infection can look like a different scalp condition in teens, leading to wrong treatment until proper tests are done.
 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Possible causes of female hair loss include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, cicatricial alopecia, and alopecia areata incognita; diagnosis and treatment require dermoscopy and histopathology.
 21 citations,
November 1981 in “Archives of Dermatology”
21 citations,
November 1981 in “Archives of Dermatology” Ashy dermatosis may be linked to atopy and thyroid disease and can be treated with topical steroids.
 10 citations,
August 2003 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
10 citations,
August 2003 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Actinic superficial folliculitis is a unique skin condition caused by intense heat and sweating.
 40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Systemic glucocorticosteroids are a primary treatment for various skin conditions but require careful management due to potential side effects and relapses.
 6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib may effectively treat Alopecia Areata.
 29 citations,
April 2013 in “Mycoses”
29 citations,
April 2013 in “Mycoses” A young man was initially misdiagnosed with a scalp condition but was found to have a fungal infection, which improved with antifungal treatment.





























