 14 citations,
January 2020 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
14 citations,
January 2020 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Some dietary supplements, like vitamins B6/B12, iodine, whey protein, and muscle-building products, can cause or worsen acne.
 June 2024 in “International journal of nanomedicine”
June 2024 in “International journal of nanomedicine” Azelaic acid micro/nanocrystals, especially with ultrasound and salicylic acid, greatly improve acne treatment.
[object Object]  15 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
15 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Start acne treatment early to prevent scarring, consider antibiotic resistance, use maintenance therapy, and manage side effects carefully.
 34 citations,
September 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
September 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Using anabolic-androgenic steroids can cause skin problems like acne and hair loss in athletes.
January 2016 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Hormonal therapy changes skin and hair in transgender patients, who need better researched dermatologic care.
 April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” RPGRIP1L helps skin cells stick together by blocking PKCβII, which can prevent skin blistering like in pemphigus.
 April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Applying the anti-cancer drug Bortezomib to skin can promote hair growth and increase hair proteins through the GATA-3 factor.
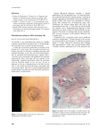 13 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
13 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” A benign tumor developed at a girl's BCG vaccination site, not previously linked to the vaccine.
6 citations,
March 1990 in “The American journal of cosmetic surgery”  January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and treatment of follicular disorders are crucial, with specific treatments for conditions like acne, drug-induced eruptions, and rosacea.
 1 citations,
December 2022 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Acne treatment with isotretinoin increases the presence of p53, a protein, in skin and oil glands, which may help reduce acne severity.
 45 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology”
45 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology” Some skin conditions look like acne but are caused by drugs, and they usually get better when the drug is stopped.
19 citations,
March 2021 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine” Isotretinoin can cause serious birth defects and needs careful use, especially in pregnant women.
 66 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
66 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Isotretinoin's effects and side effects, like birth defects and depression, might be due to it causing cell death in various cells.
 138 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
138 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Eating less sugar, milk, and saturated fats and more vegetables and fish may help treat and prevent acne.
 78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal”
78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Acne treatment varies, with topical and systemic therapies effective, and more research needed on treatment order and long-term effects.
 99 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
99 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that certain genetic mutations and dietary factors are involved in acne development, and treatments like isotretinoin and diet changes can help manage it.
 93 citations,
January 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
93 citations,
January 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Eating a high-glycemic diet may worsen acne by increasing certain protein levels and expressions in the skin.
 14 citations,
April 2014 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
14 citations,
April 2014 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Acne is caused by multiple factors including oil production, bacteria, inflammation, and possibly diet and environment.
 11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology”
11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology” Acne and increased body hair in teenage girls are normal but severe cases may need hormone evaluation and treatment can prevent diabetes linked to PCO.
 3 citations,
January 2018 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
3 citations,
January 2018 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Longer TA repeats in the SRD5A2 gene may increase acne risk in Chinese people.
 3 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Society (Print)”
3 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Society (Print)” Acne is common in adult women, often continues from adolescence, and can lead to scarring.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne is linked to inflammation and insulin resistance, and is associated with various syndromes that require different treatments.
 November 2014 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks”
November 2014 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks” Eating high-glycemic and dairy foods can increase hormones that may cause acne and other health issues.
 97 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”
97 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders” The sebaceous gland has more roles than just producing sebum and contributing to acne, and new research could lead to better skin disease treatments.
 65 citations,
February 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
65 citations,
February 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Anti-acne medications may work by reducing the activity of a protein involved in acne development.
[object Object]  25 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Endocrinology/Journal of endocrinology”
25 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Endocrinology/Journal of endocrinology” Human sebaceous glands contain enzymes that affect androgen production and may influence sebum production and acne.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “Experimental dermatology”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “Experimental dermatology” New imaging techniques can assess and track changes in mouse acne without harm, aiding treatment choices.
1 citations,
February 2024 in “Cosmetics” Cannabidiol shows promise as an effective treatment for acne.
 July 1975 in “Archives of Dermatology”
July 1975 in “Archives of Dermatology” The document suggests a possible connection between rapid weight loss and hair loss, and reports a case of skin condition improvement after stopping acne medication.


























