 2 citations,
May 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
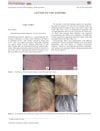
May 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Some patients' hair grew back black and white after chemotherapy.
 1 citations,
October 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in a drug reaction case involved both a common shedding phase and an immune attack on hair follicle stem cells.
 January 2022 in “Medical research archives”
January 2022 in “Medical research archives” Taking vitamin D might improve life for MS patients and reduce skin side effects from alemtuzumab treatment.
[object Object]  January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology” A woman developed severe kidney injury from using simvastatin with ciclosporin, highlighting the need for careful monitoring when combining these drugs.
 218 citations,
January 2013 in “The Lancet Oncology”
218 citations,
January 2013 in “The Lancet Oncology” Chemotherapy causes hair loss by damaging hair follicles and stem cells, with more research needed for prevention and treatment.
 183 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International”
183 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International” AA-PRP injections effectively increase hair count and thickness for male pattern hair loss.
 162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Latanoprost can make eyelashes longer, thicker, and darker.
 147 citations,
September 2006 in “Developmental Cell”
147 citations,
September 2006 in “Developmental Cell” Too much Smad7 changes skin and hair development by breaking down a protein called β-catenin, leading to more oil glands and fewer hair follicles.
 103 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
103 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Chemotherapy often causes temporary hair loss, which is distressing and needs better treatment and support.
 76 citations,
August 2007 in “Supportive care in cancer”
76 citations,
August 2007 in “Supportive care in cancer” Chemotherapy often causes skin, nail, and hair side effects, significantly impacting quality of life.
 76 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Molecular Medicine”
76 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Molecular Medicine” Certain mice without specific receptors or mast cells don't lose hair from stress.
 64 citations,
July 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
64 citations,
July 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Scalp cooling can prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss, and certain treatments can speed up hair regrowth, but more research is needed for better treatments.
 62 citations,
February 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology”
62 citations,
February 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology” Scalp cooling can reduce chemotherapy-induced hair loss and should be available in all hospitals.
 58 citations,
January 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
58 citations,
January 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Different methods of preparing Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) can affect wound healing and hair regrowth in plastic surgery. Using a kit with specific standards helps isolate PRP that meets quality criteria. Non-Activated PRP and Activated PRP have varying effects depending on the tissue and condition treated. For hair regrowth, Non-Activated PRP increased hair density more than Activated PRP. Both treatments improved various aspects of scalp health.
 53 citations,
January 2007 in “Dermatology”
53 citations,
January 2007 in “Dermatology” Chemotherapy often causes patterned hair loss, with some scalp areas more resistant to hair loss than others.
 48 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
48 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The conclusion is to use scalp cooling, gentle hair care, and treatments like minoxidil for managing hair loss from chemotherapy, and stresses the need for more research and collaboration in this area.
 44 citations,
November 2010 in “Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care”
44 citations,
November 2010 in “Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care” Many patients find hair loss from chemotherapy very distressing, and while treatments like minoxidil and scalp cooling may help, there is no sure way to prevent it.
 39 citations,
December 2001 in “JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute”
39 citations,
December 2001 in “JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute” Using a gene therapy with the Sonic Hedgehog gene helps mice regrow hair faster after losing it from chemotherapy.
 38 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncologist”
38 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncologist” Scalp cooling can help prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss with a 50-90% success rate and is safe for patients.
 34 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Scalp cooling is the most effective FDA-approved method to prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss, but more research is needed for other treatments.
 32 citations,
May 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
32 citations,
May 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice without collagen VI have slower hair growth normally but faster regrowth after injury.
 30 citations,
September 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
September 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology” Minoxidil helps prevent stress-caused hair loss in mice.
 28 citations,
December 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
28 citations,
December 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Some medications might reverse gray hair, especially those that reduce inflammation or stimulate pigment production, and vitamin B might help.
 28 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of Drug Targeting”
28 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of Drug Targeting” The new CoQ10 gel protects mouse skin better against aging from UV light than the old gel.
[object Object]  26 citations,
January 1992 in “Cancer investigation”
26 citations,
January 1992 in “Cancer investigation” N-acetylcysteine and ImuVert can prevent hair loss in rats caused by chemotherapy.
 24 citations,
June 2011 in “Andrologia”
24 citations,
June 2011 in “Andrologia” Ganoderma lucidum may help treat enlarged prostate in rats.
 23 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
23 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Chemotherapy caused hair loss with specific patterns, but most patients had hair regrowth after treatment, while some had lasting hair loss.
 20 citations,
September 2013 in “Anti-Cancer Drugs”
20 citations,
September 2013 in “Anti-Cancer Drugs” PTH-CBD could help prevent and treat hair loss caused by chemotherapy in mice.
 19 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” CD3+ T-cell presence is a reliable marker to tell apart alopecia areata from pattern hair loss.
 19 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Ginseng Research”
19 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Ginseng Research” Korean Red Ginseng may protect against hair loss caused by chemotherapy.






























