May 2022 in “Brazilian Journal of Health Review” COVID-19 infection can cause temporary hair loss due to stress, treatment drugs, psychological impact, and pandemic-related stress.

Melatonin may improve hair growth by affecting certain cell signaling pathways.
Melatonin improves hair growth-related cell properties by activating a certain cell signaling pathway.
 April 2022 in “Brazilian Medical Students”
April 2022 in “Brazilian Medical Students” People with androgenetic alopecia may have a higher risk of severe COVID-19.
 January 2022 in “Figshare”
January 2022 in “Figshare” Melatonin affects when and how goat hair follicle genes turn on and off during growth cycles.
 November 2021 in “Pharmaceutical Sciences”
November 2021 in “Pharmaceutical Sciences” New compounds were made and tested, with compound 6 showing potential for treating prostate-related diseases.
October 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking IL-12 can help treat alopecia areata by preventing hair follicle immune issues.
 June 2021 in “Aesthetic Cosmetology and Medicine”
June 2021 in “Aesthetic Cosmetology and Medicine” Some people lose a lot of hair after having COVID-19.
April 2021 in “Libyan journal of medical sciences” A woman's hair loss improved with treatment after a COVID-19 infection.
 March 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
March 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Removing a specific gene in certain skin cells causes hair loss on the body by disrupting normal hair development.
 July 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
July 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The enzymes Tet1, Tet2, and Tet3 are important for the development of hair follicles and determining hair shape by controlling hair keratin genes.
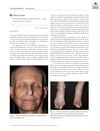 March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Rothmund-Thomson syndrome type 2 can cause chronic, poorly healing wounds.

A protein called sFRP4 can partly inhibit hair growth.

A natural compound called VB-1 can help promote hair growth by boosting a specific cell signal in human skin cells.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Nicotinic acid reduces excessive oil production in skin cells by activating a specific receptor, which could help treat acne.
Researchers improved mouse skin cell culture methods and created a similar immortal cell line, but need to clarify their methods and benefits.

The review suggested the study needed to clarify its purpose, compare with non-immortalized cells, and provide more details on methods.
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” 5α-reductase-2 deficiency causes ambiguous genitalia at birth and affects male sexual development, but individuals often develop male characteristics at puberty.

Two nutritional supplements improved hair growth and reduced hair loss in women with hair loss conditions.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology” A chemical called 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine caused rapid hair loss in mice by killing certain skin cells through a specific cell death pathway.

The peer review highlighted the need for clearer data handling, questioned the study's validity, and recognized improvements from the original version.

Reviewers suggested the study on finding new drug uses through social media side-effects needs better methods and clearer limitations.
 January 2016 in “International journal of reproduction, contraception, obstetrics and gynecology”
January 2016 in “International journal of reproduction, contraception, obstetrics and gynecology” A certain gene variation is linked to a higher risk of polycystic ovarian syndrome in South Indian women.
 May 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
May 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Researchers found a new area on chromosome 2 linked to a genetic hair loss condition.
January 2015 in “프로그램북(구 초록집)” Epiduo® is an effective first-line acne treatment that reduces inflammation and combats antibiotic resistance.

The research found that people's hair proteins vary, especially by ethnicity and body part, which could help identify individuals in forensic science.
rhKGF2 significantly promotes hair growth and follicle development.
January 2009 in “한방재활의학과학회지” Saengbal-eum-2 promotes hair growth and reduces inflammation in mice.
March 1996 in “Hair transplant forum international” April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” TGFβ-2 may cause hair loss in androgenetic alopecia.




















